Villa Savoye (outdoor photos)
Large collection of exterior photographs
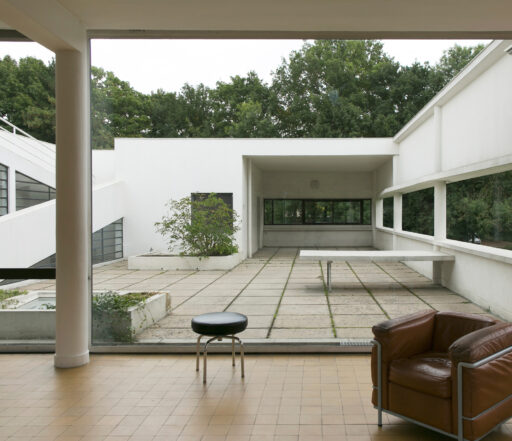
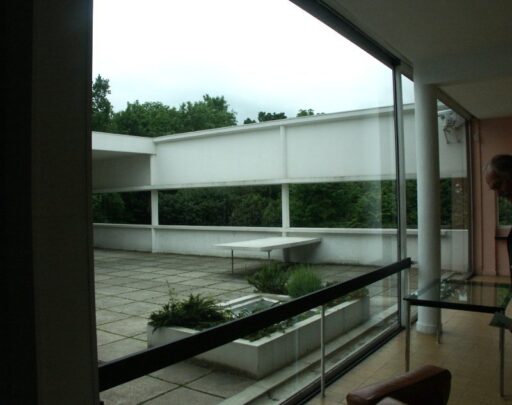
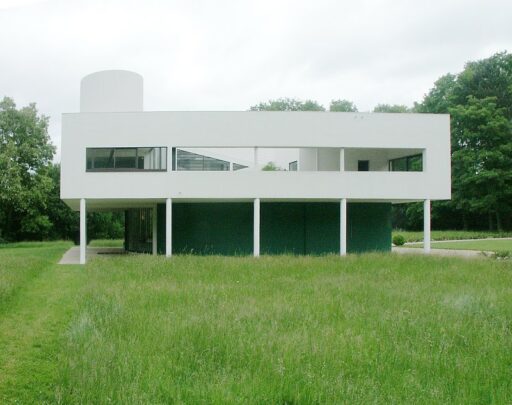
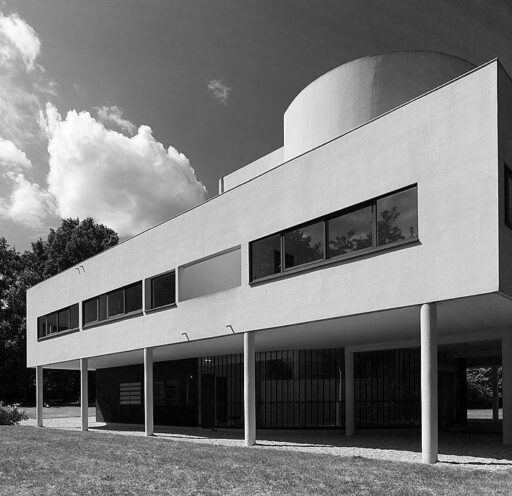
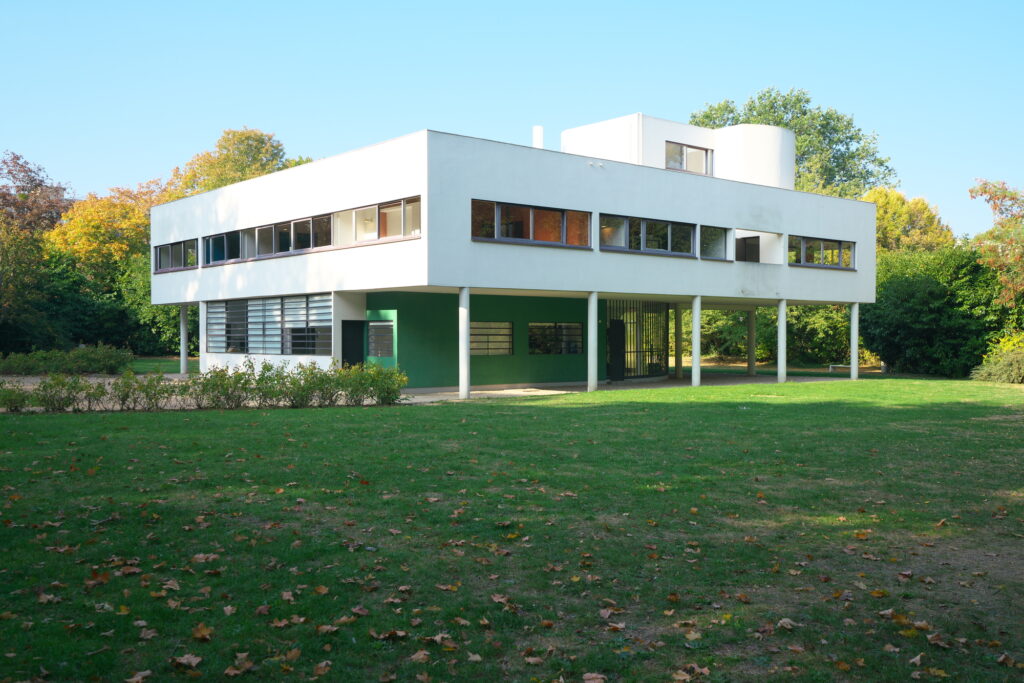
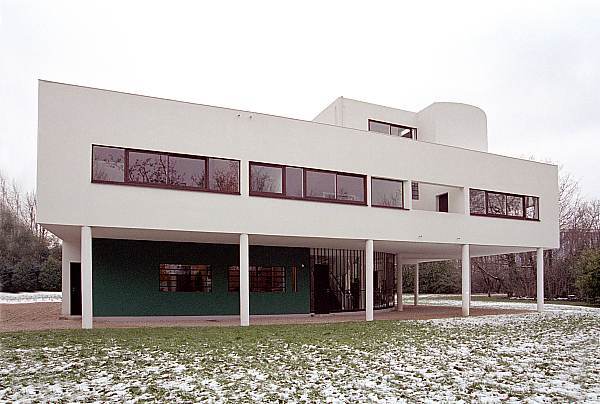
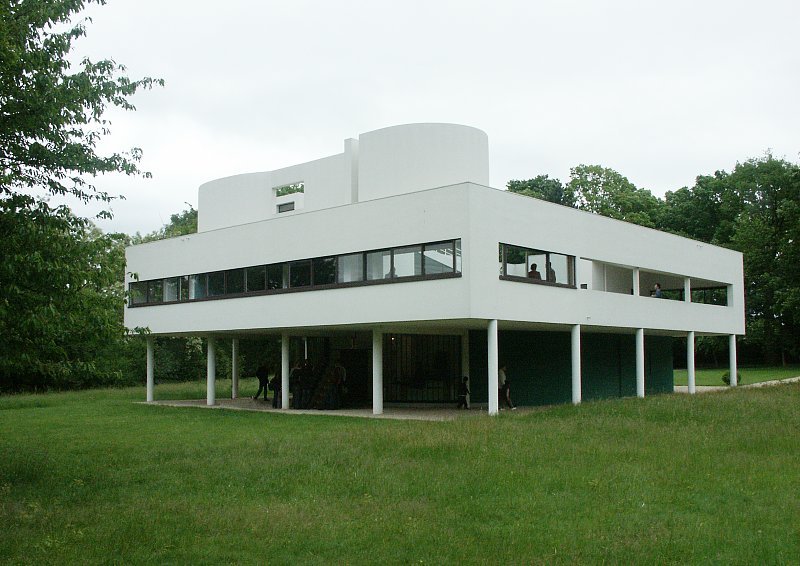
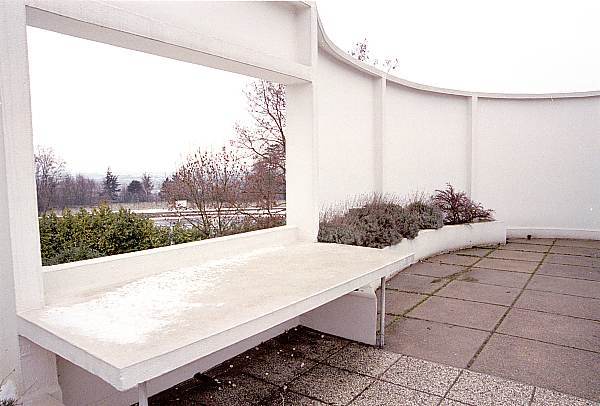
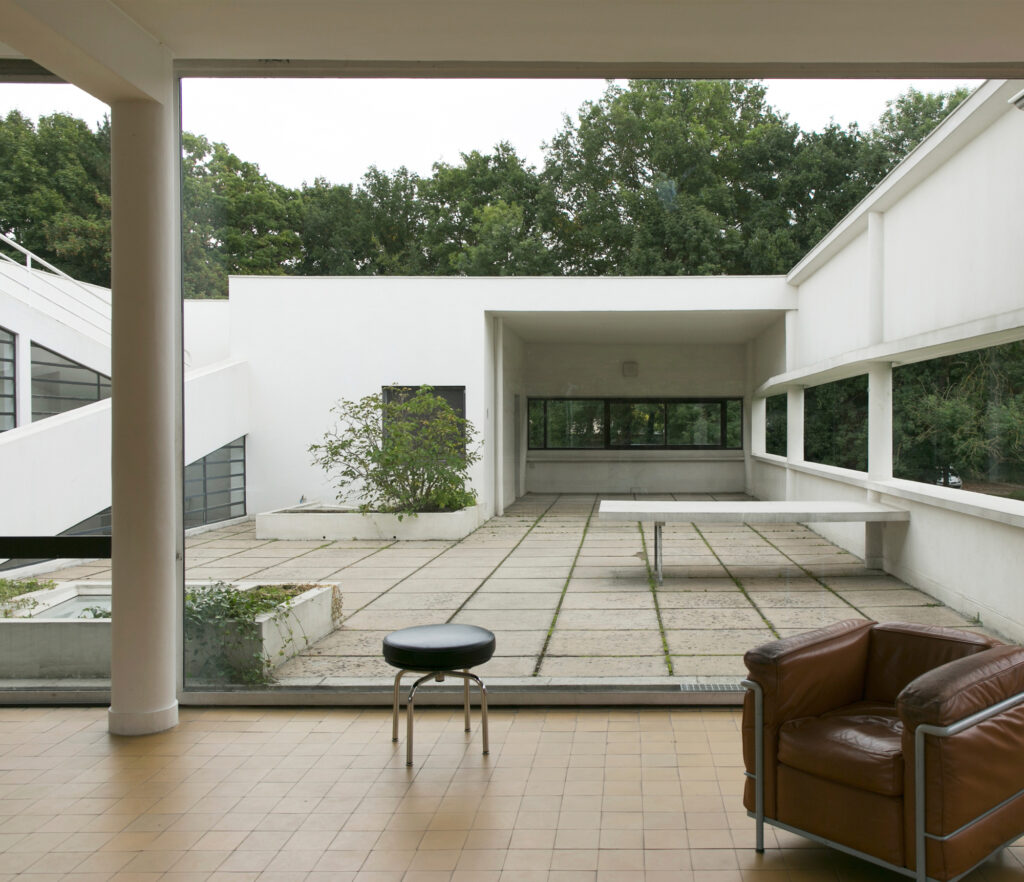
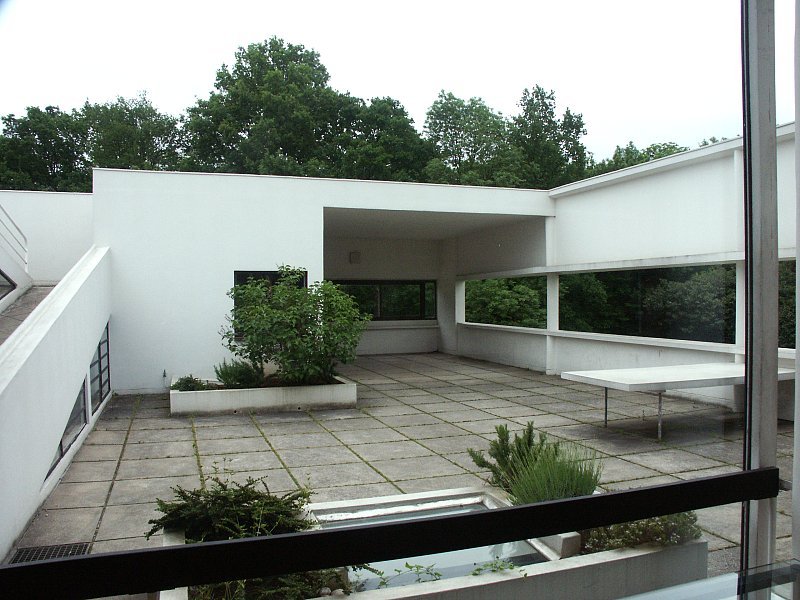
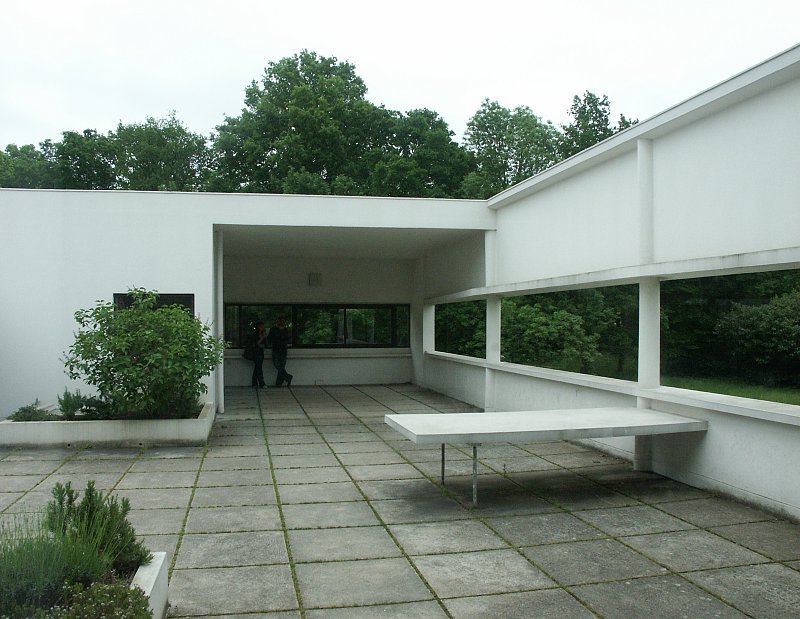
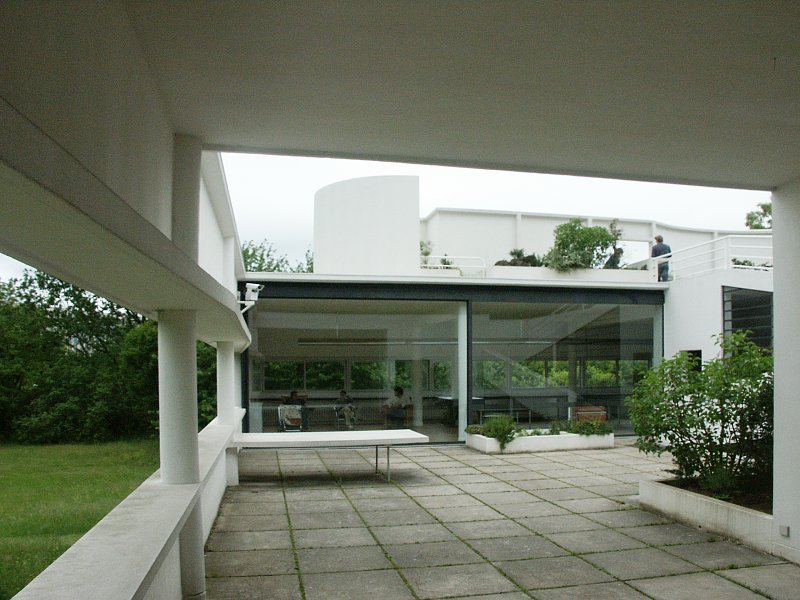
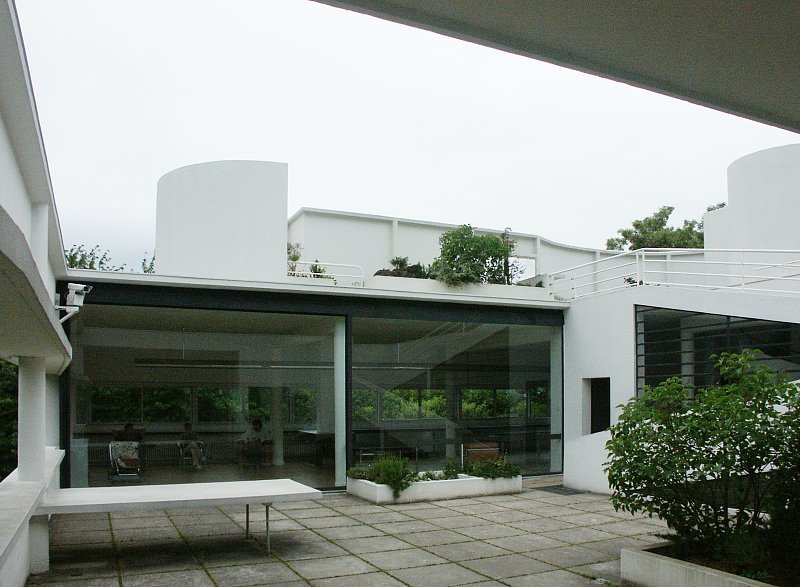
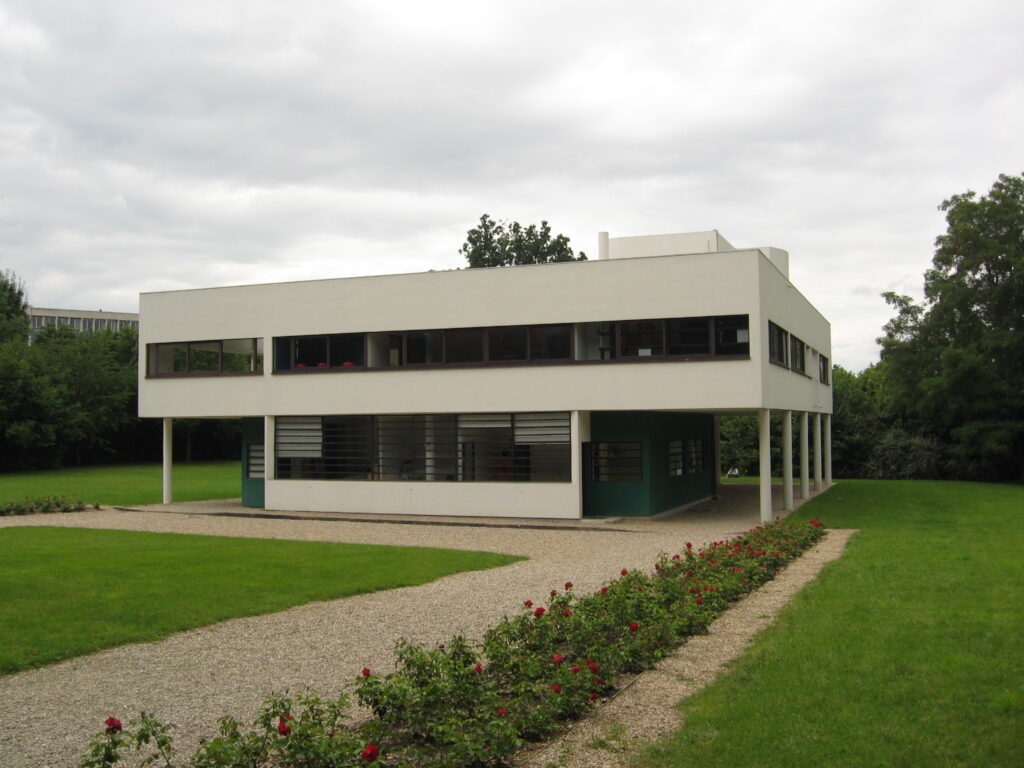
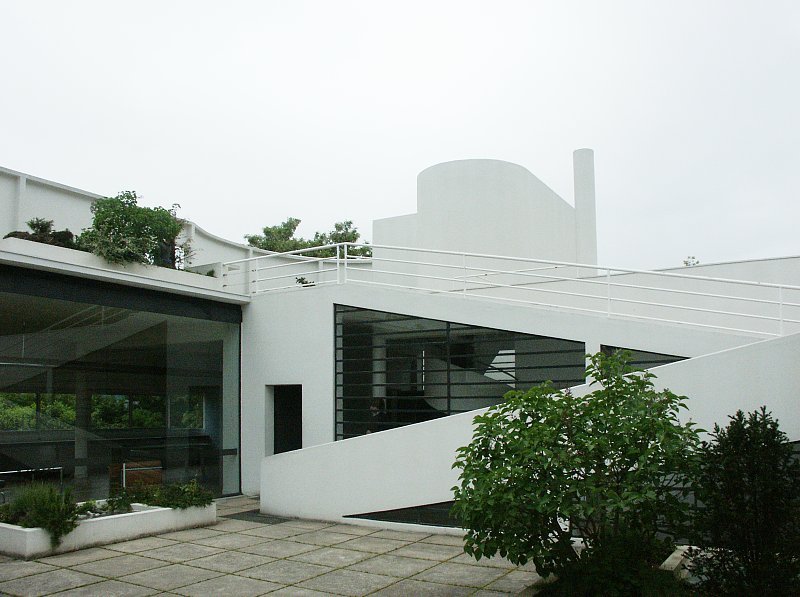
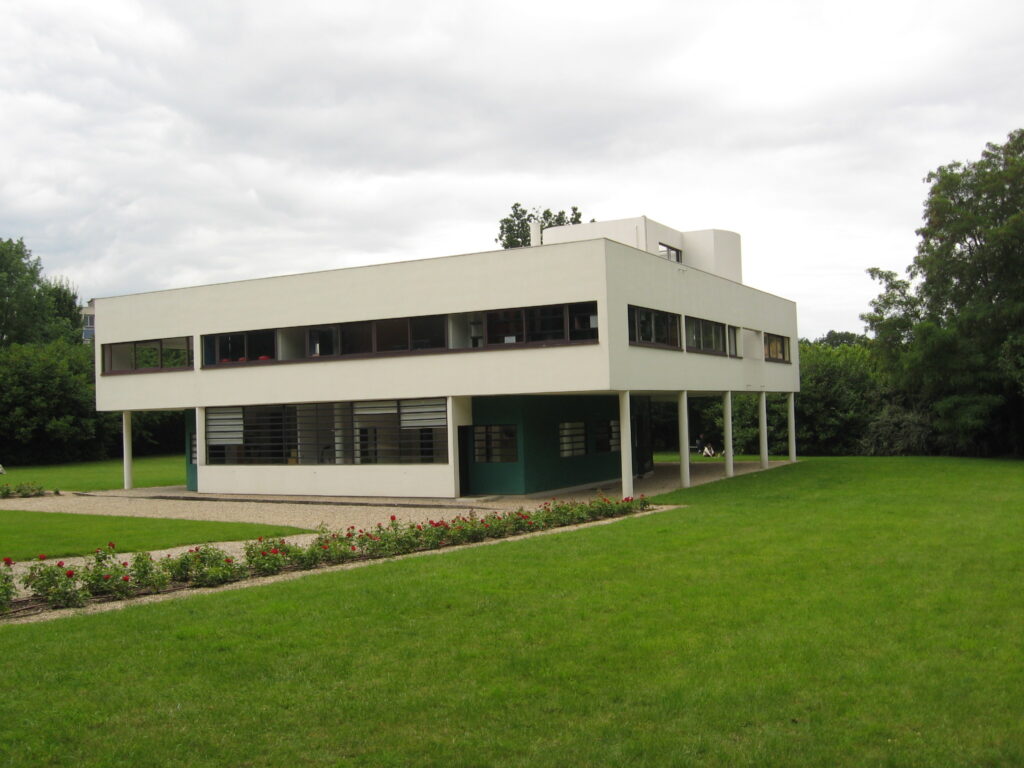
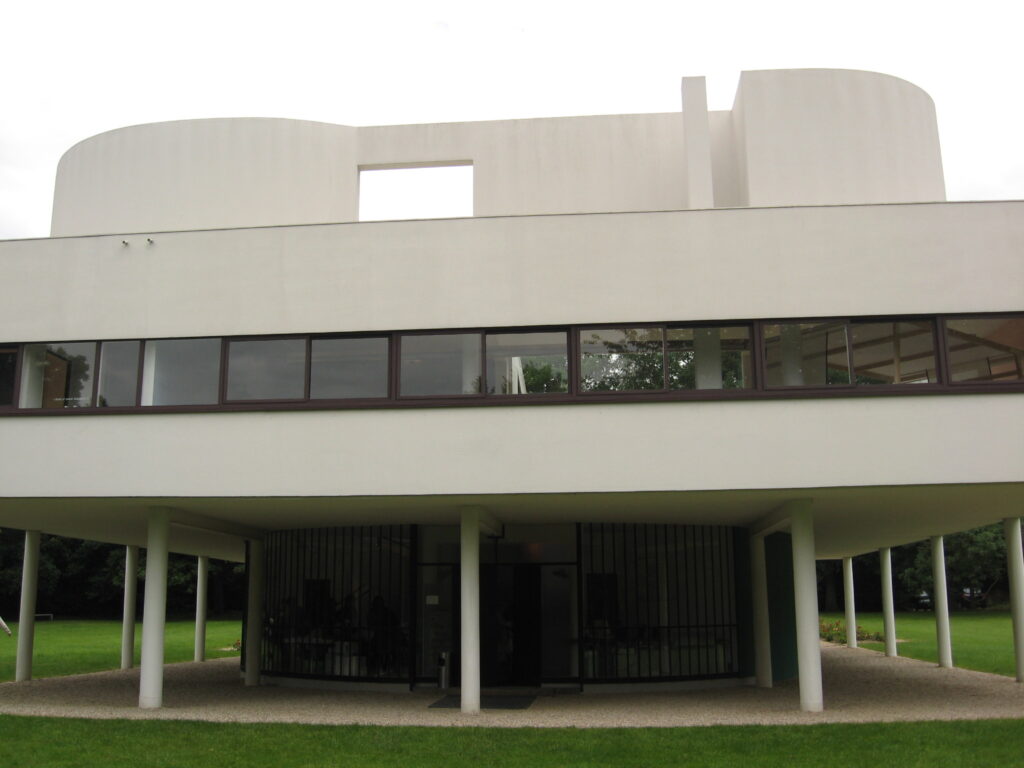
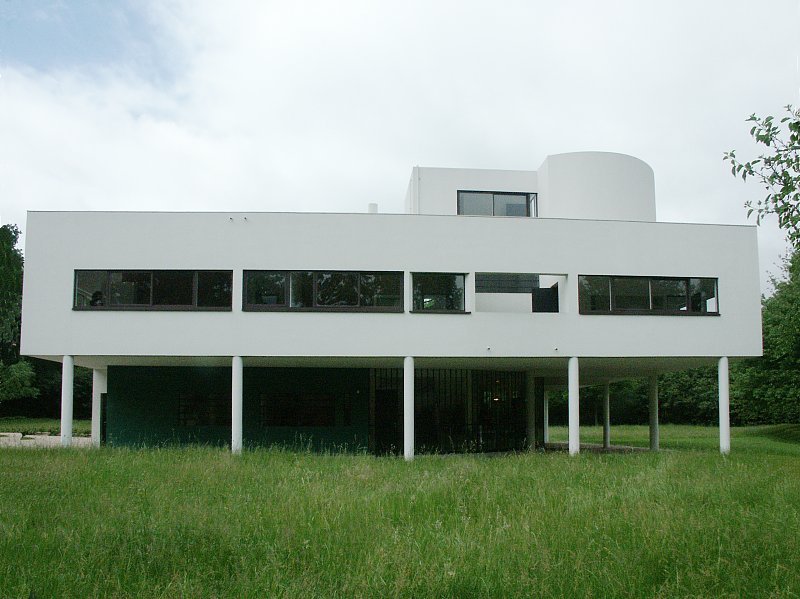
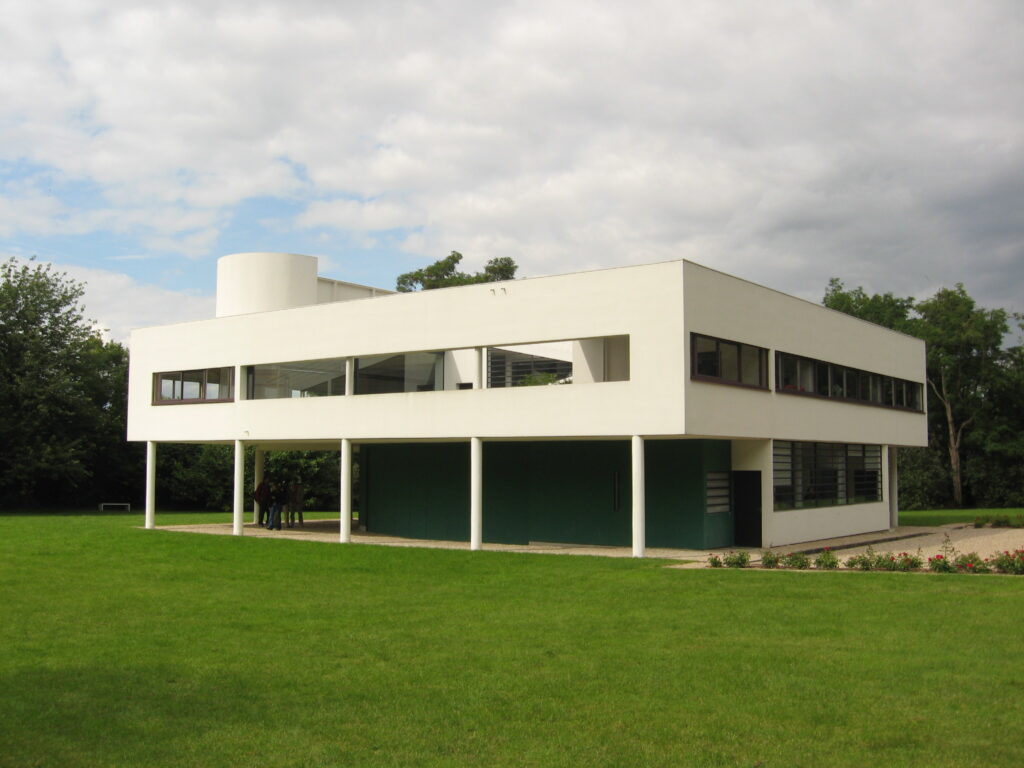
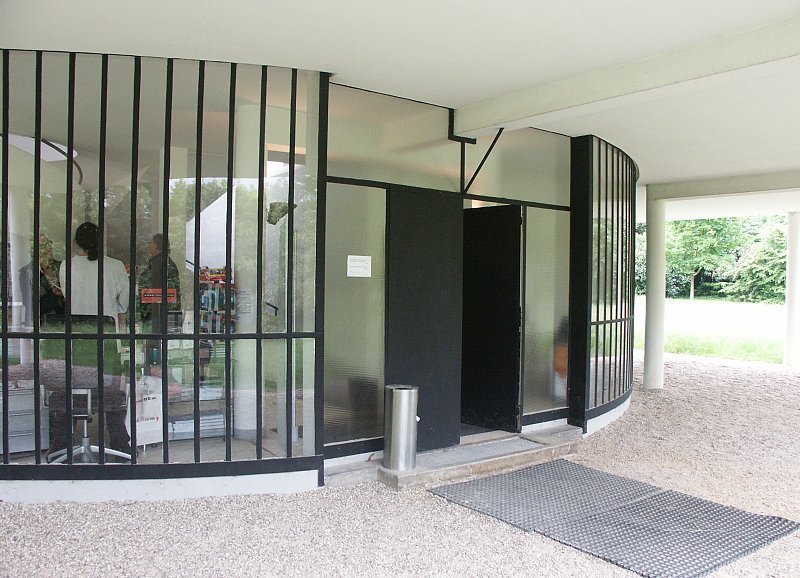
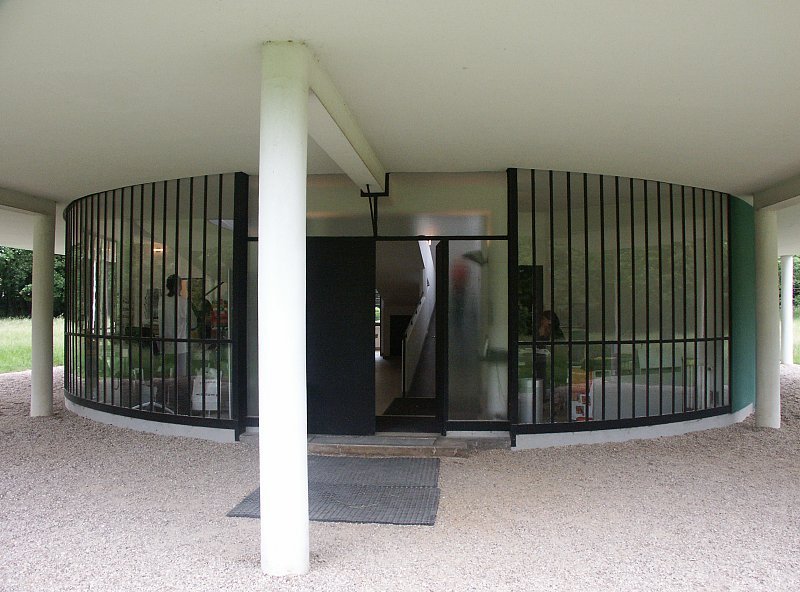
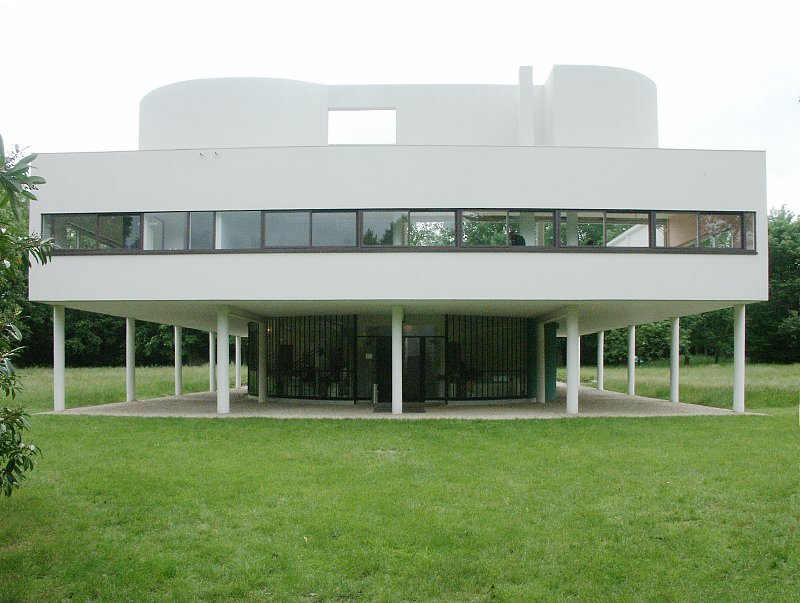
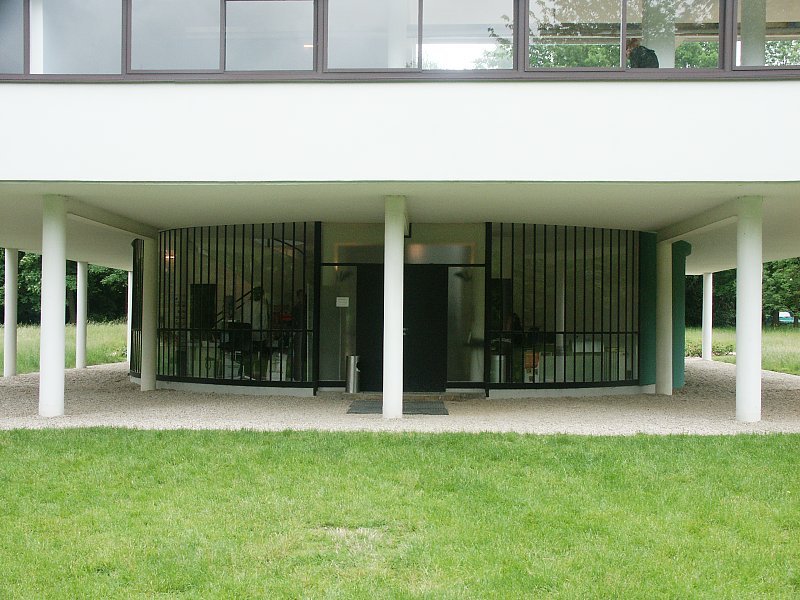
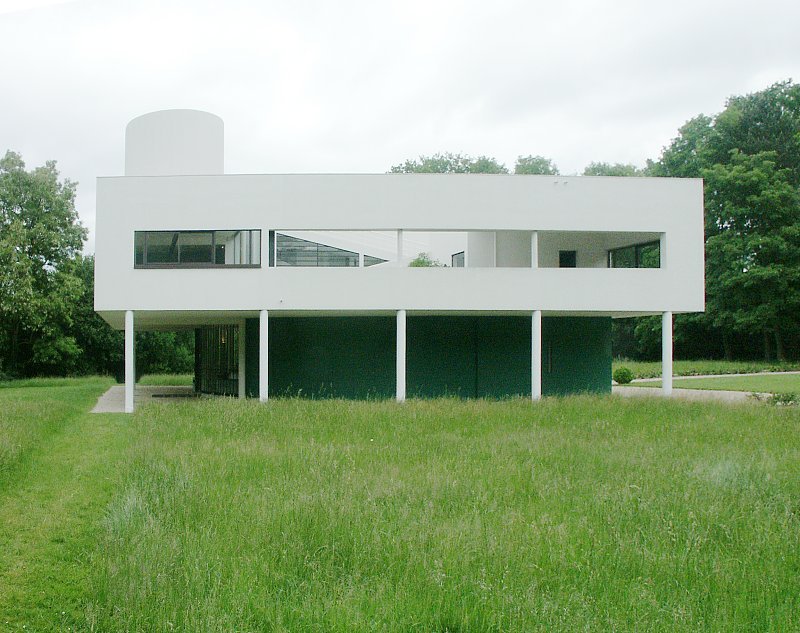
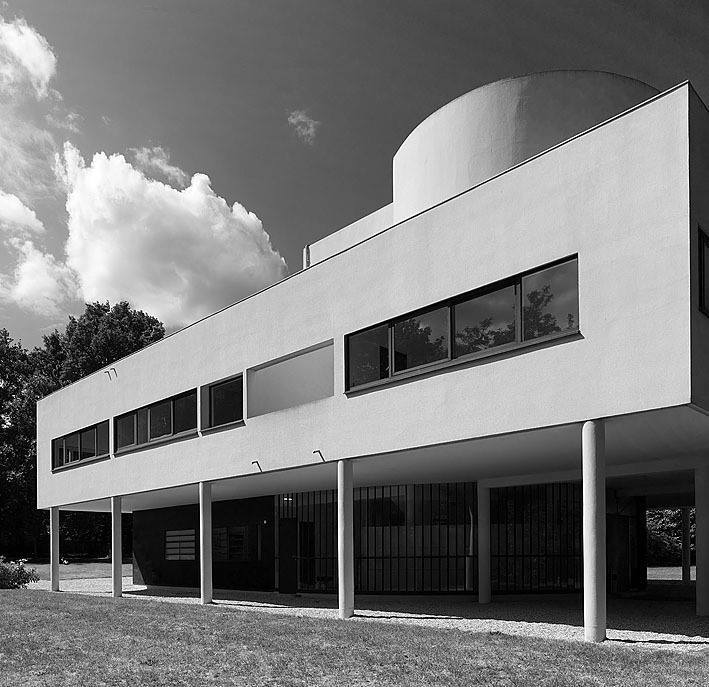
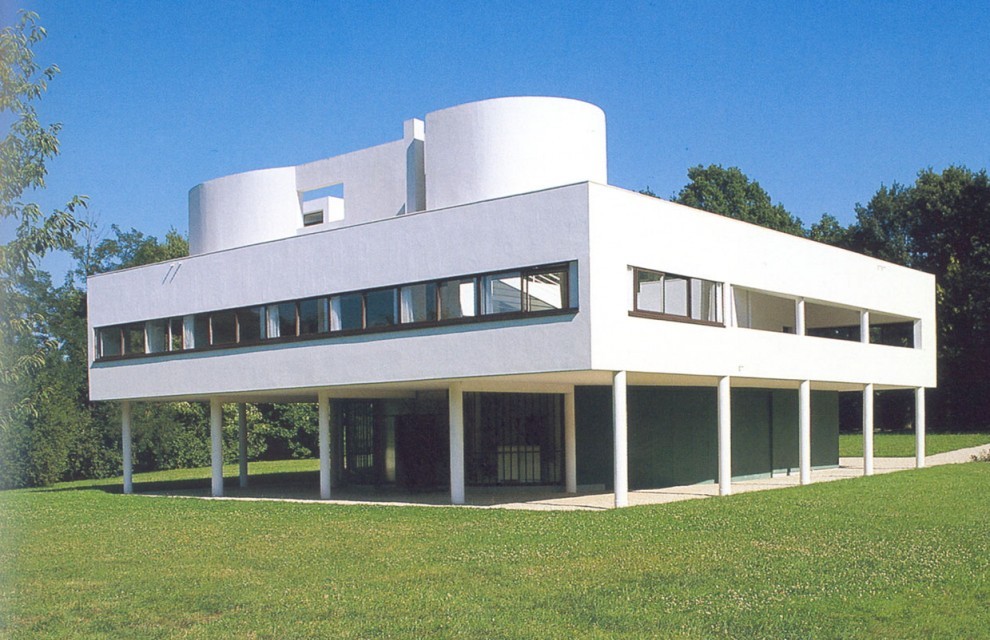
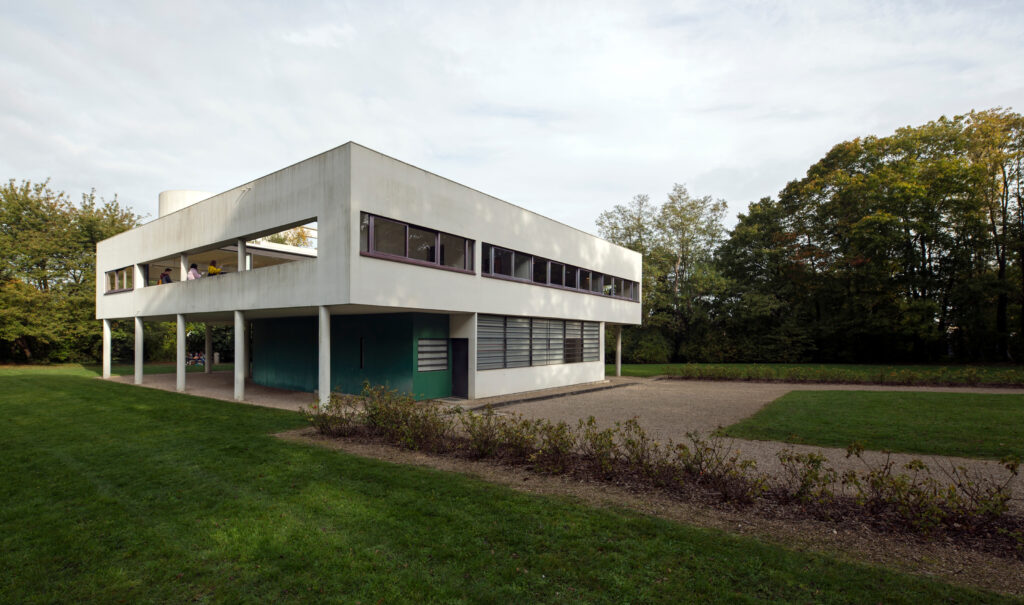
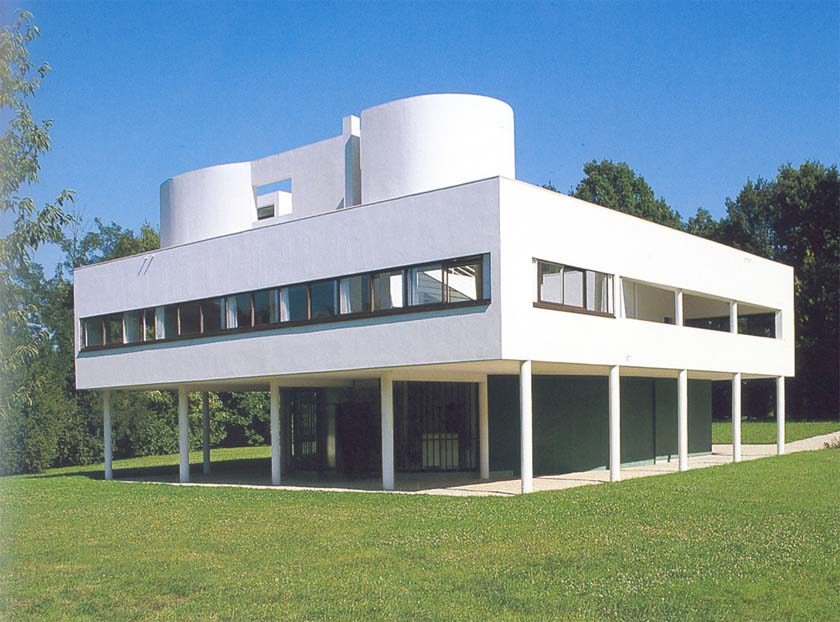
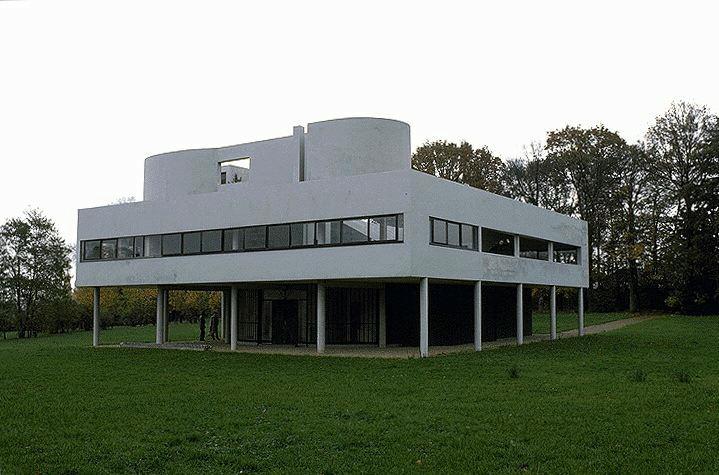
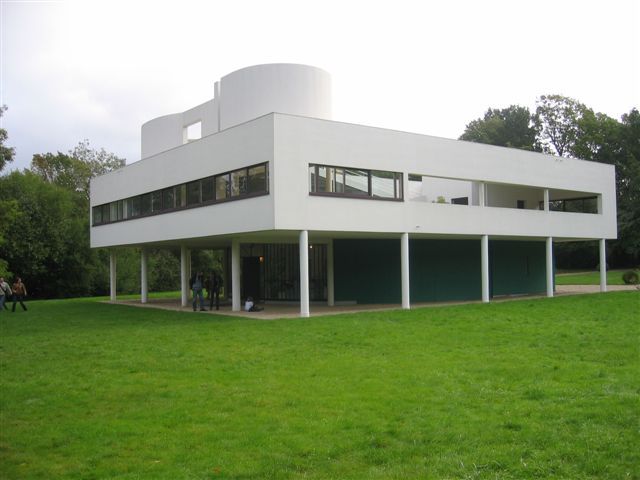
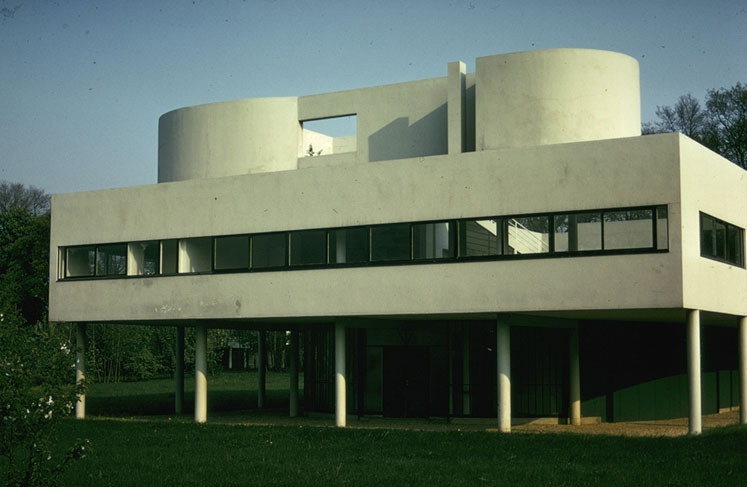
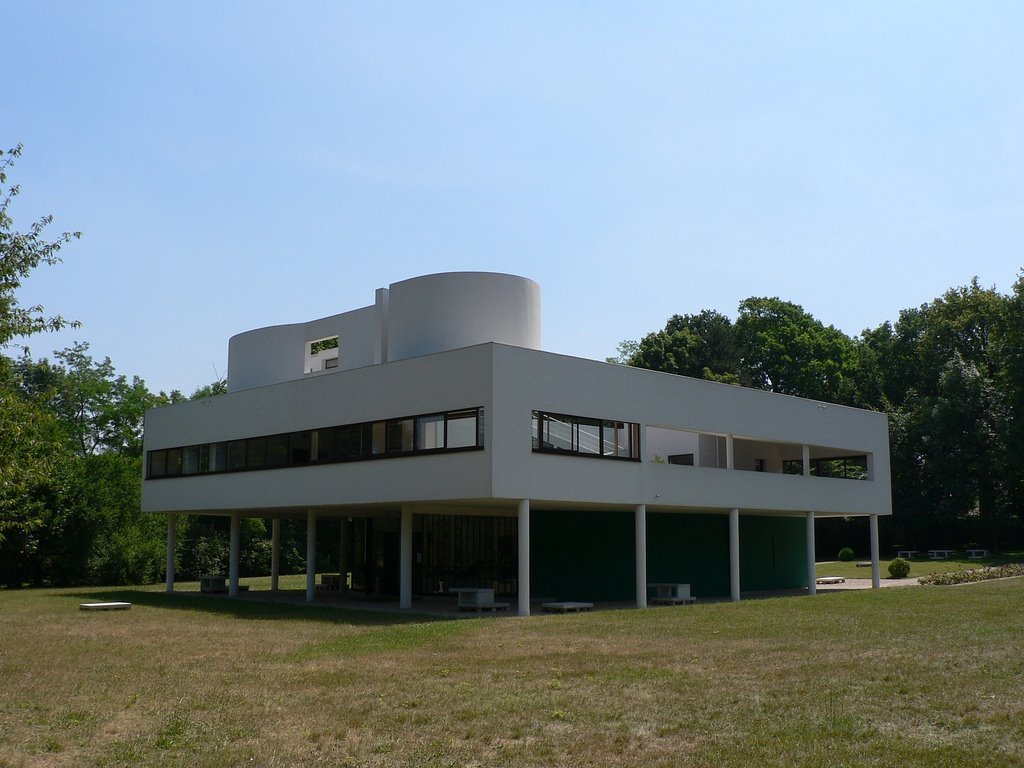
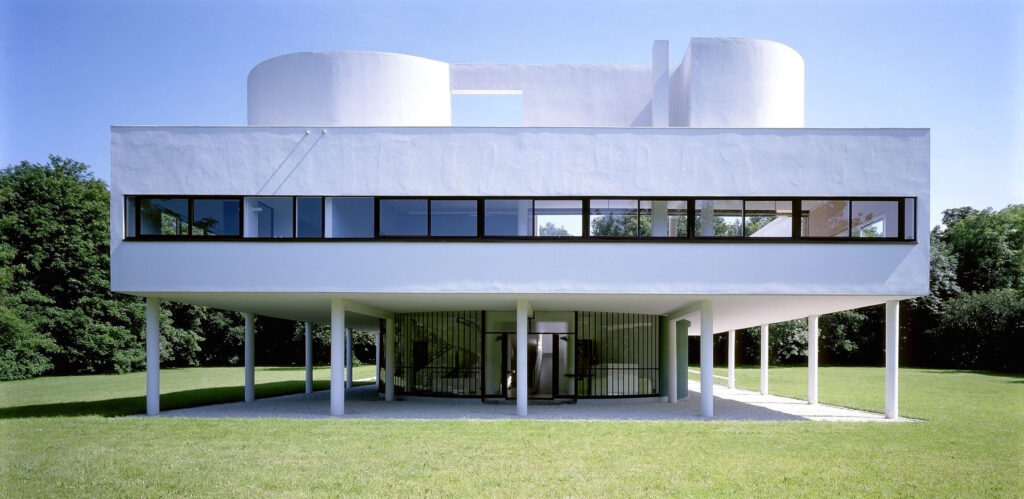
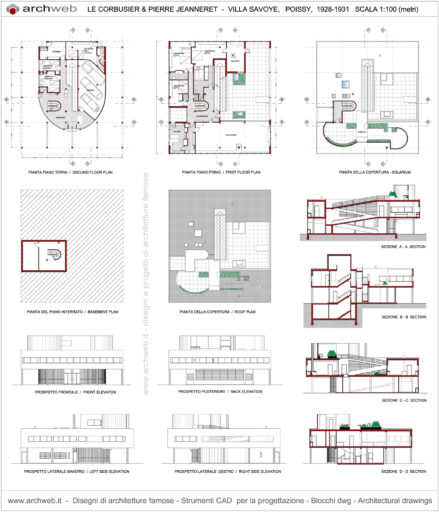
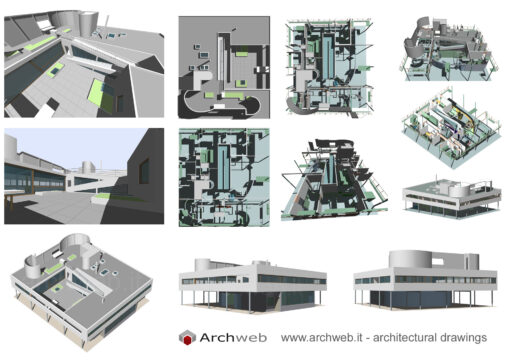
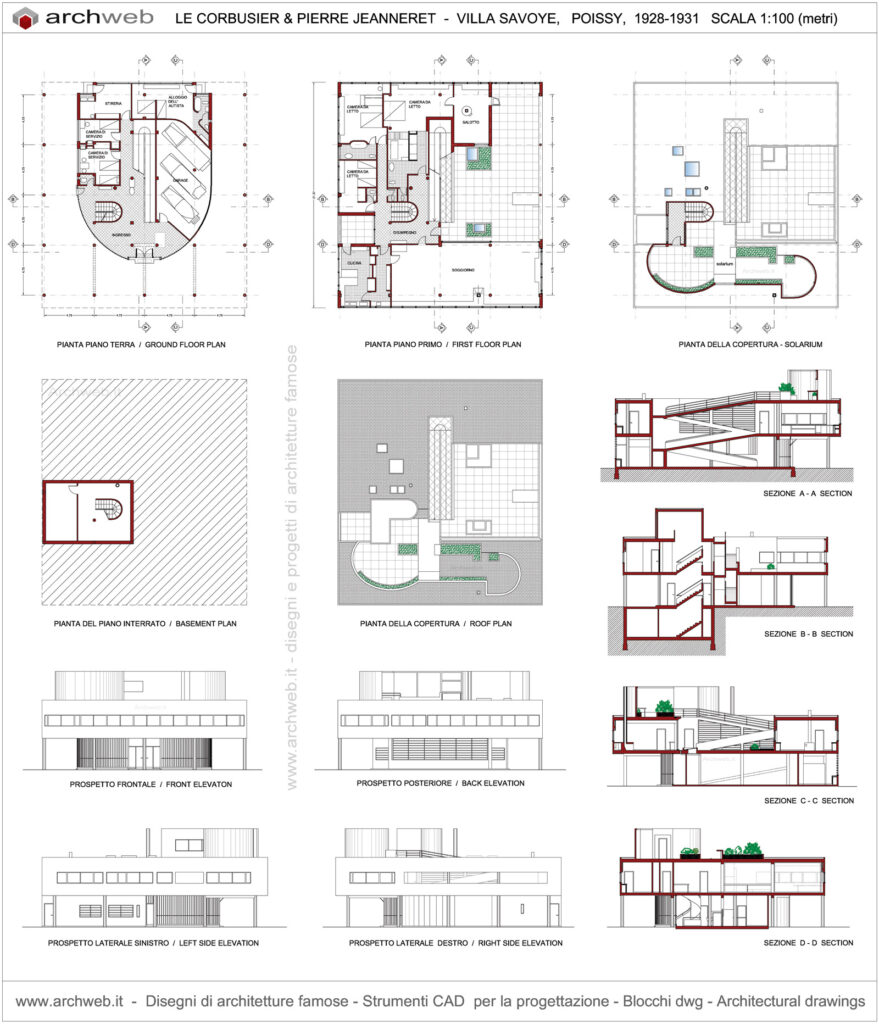
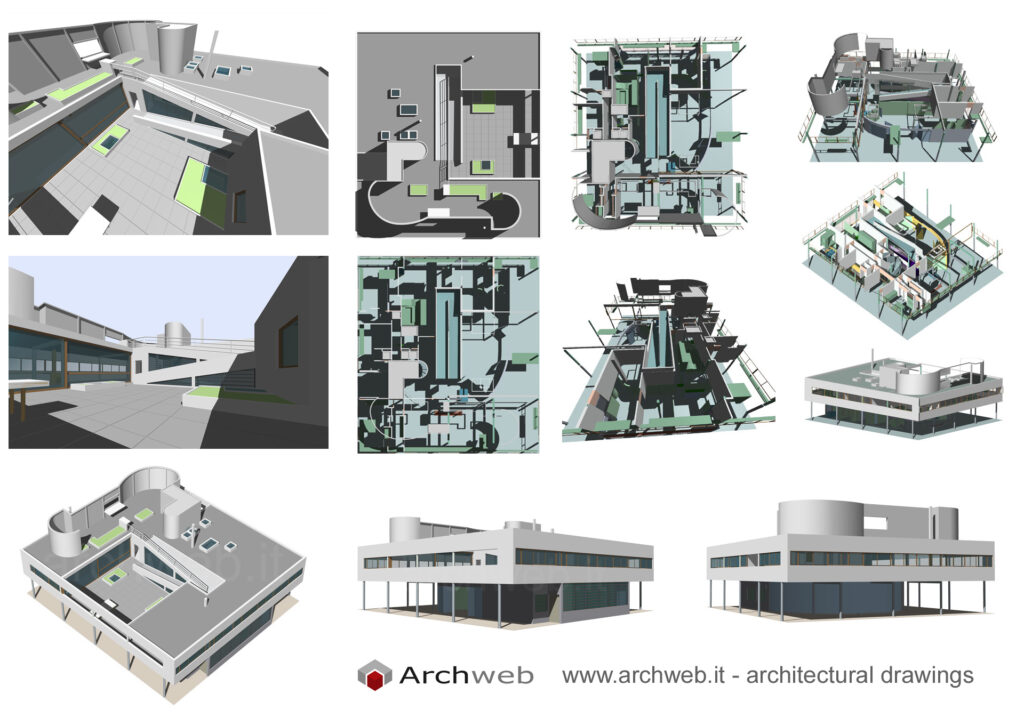
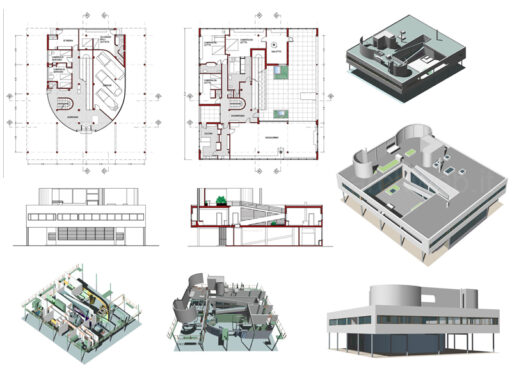
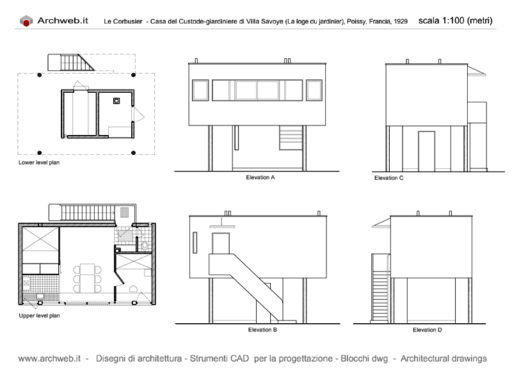
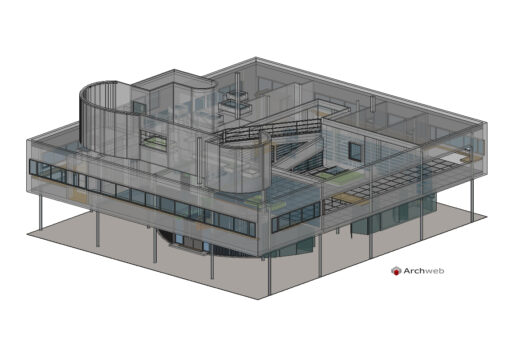
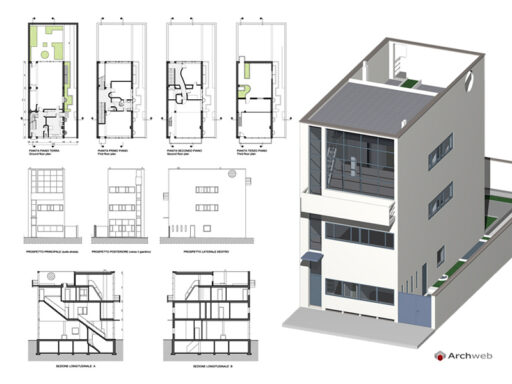
Villa Savoye is a private residence located in Poissy in the Parisian banlieue, designed by Le Corbusier (pseudonym Charles-Eduard Jeanneret-Gris), master of rationalist architecture, and by Pierre Jeanneret, built between 1928 and 1931 on commission by Pierre Savoye. It is the most famous manifesto of the modern movement and in particular of architectural cubism. It is among the monuments considered to be part of the 20th century.
The villa is known for Le Corbusier's five architectural principles:
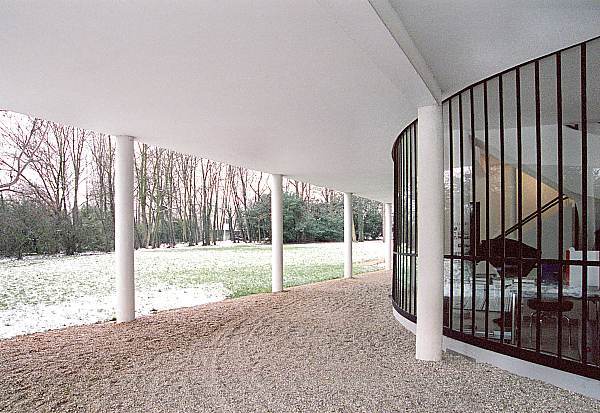
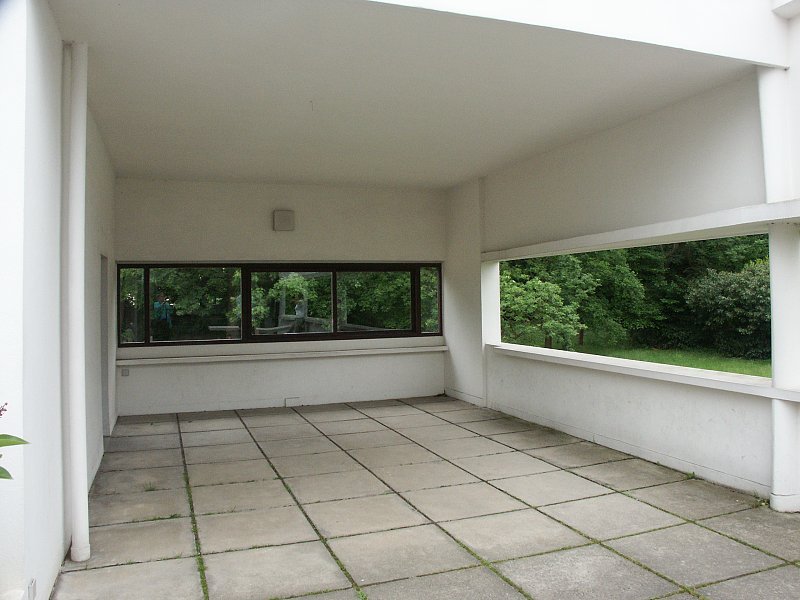
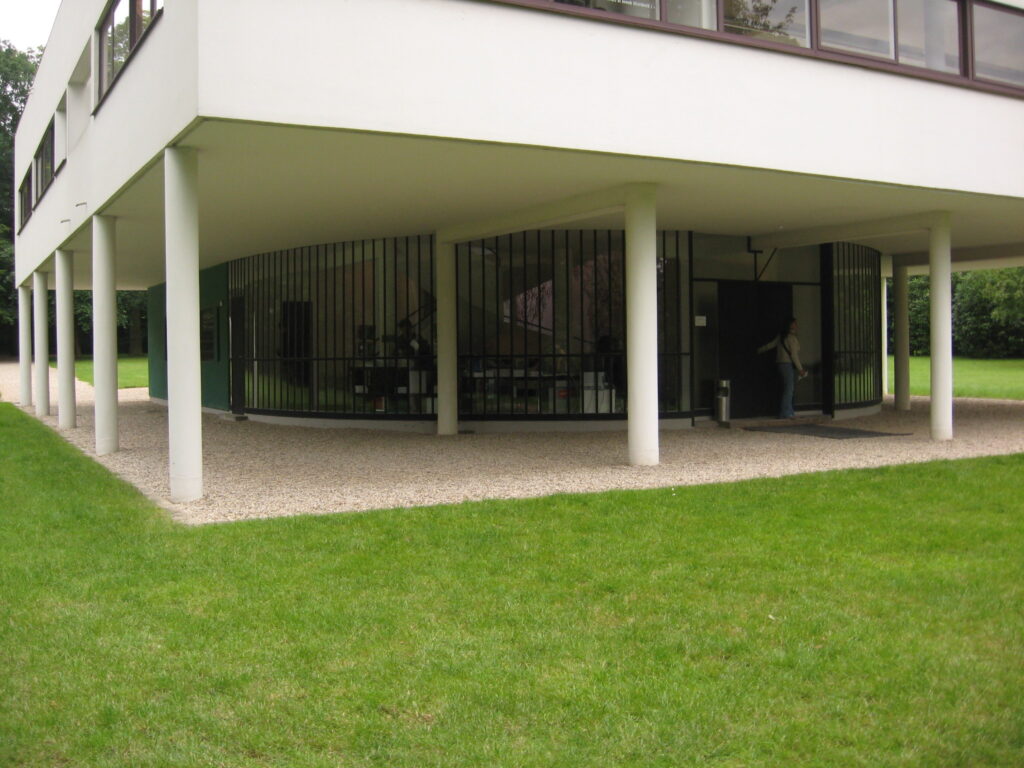
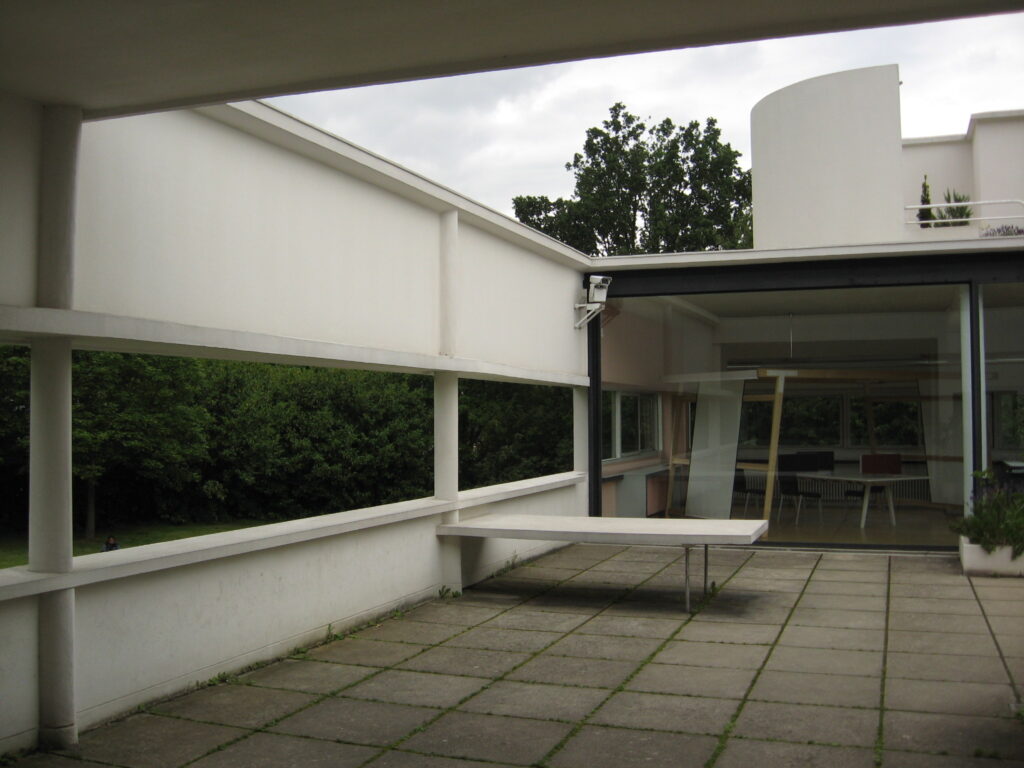
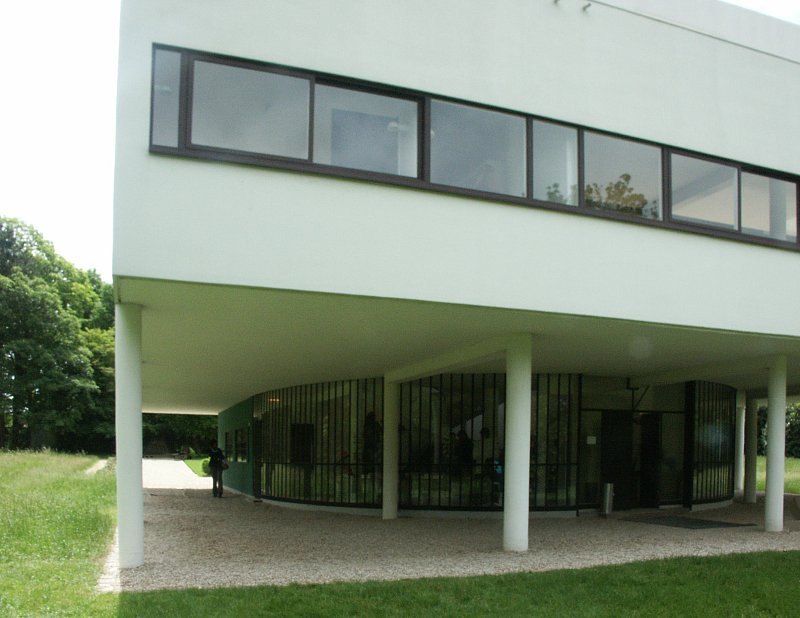
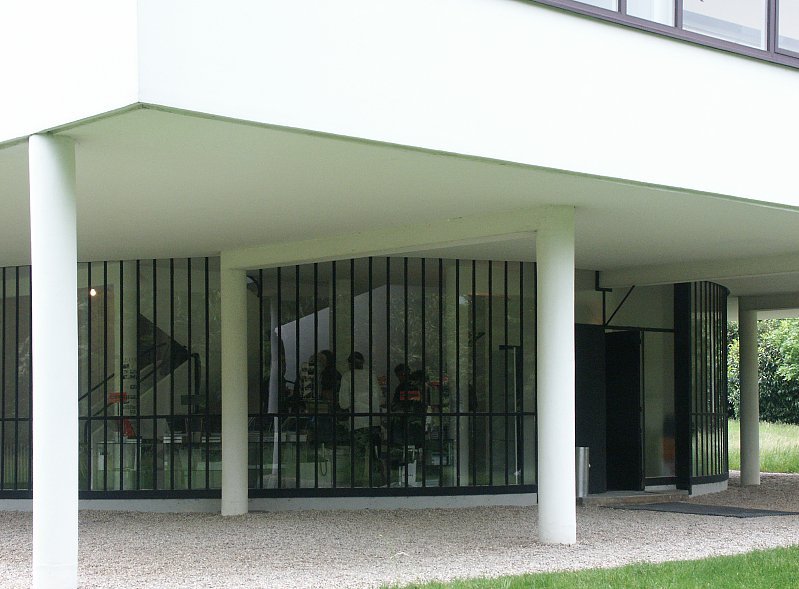
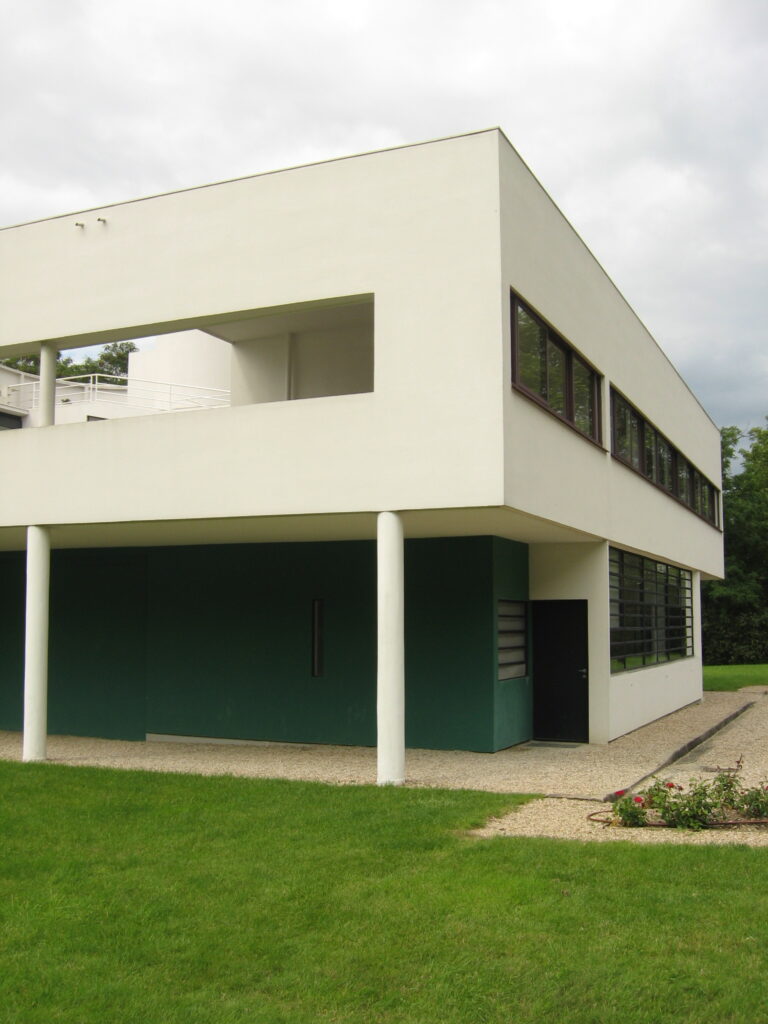
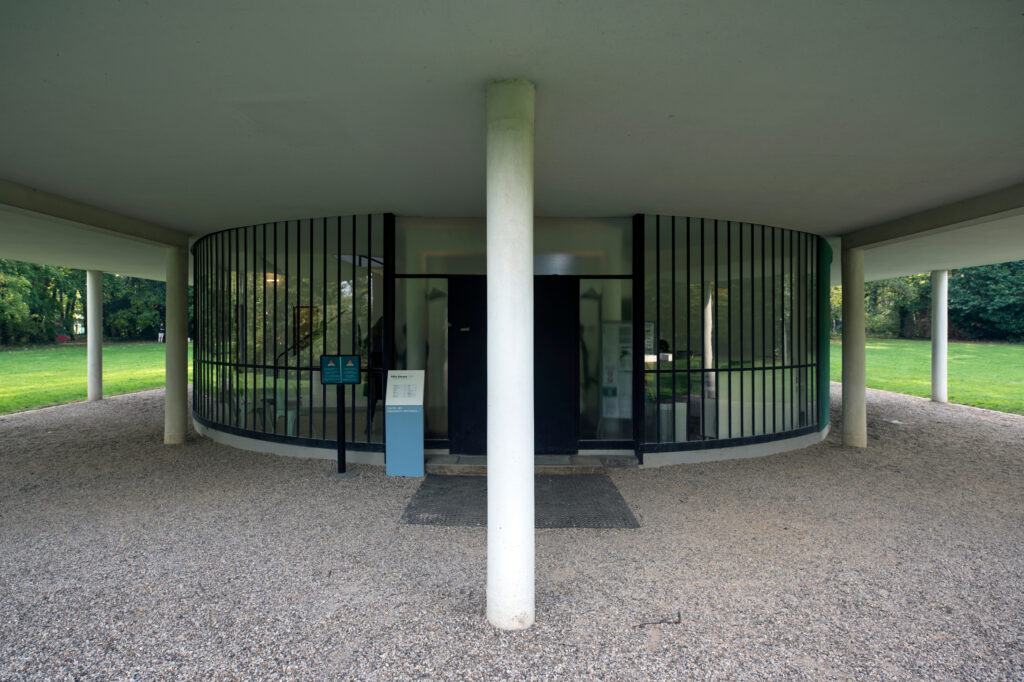
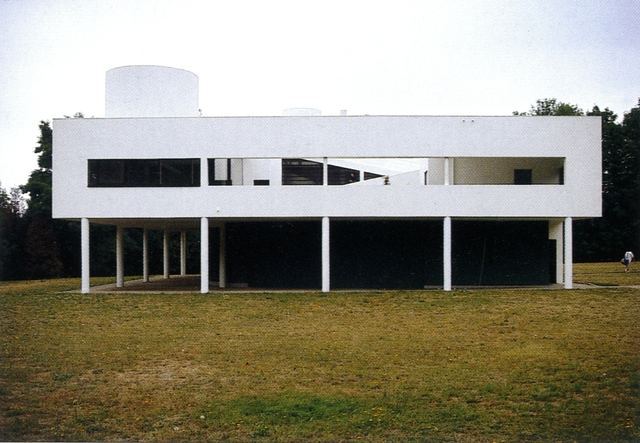
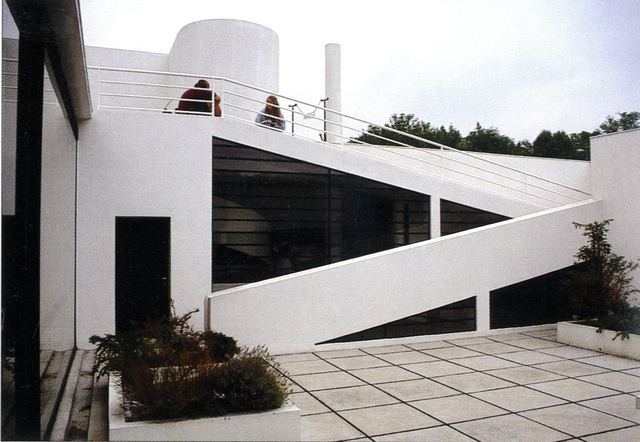
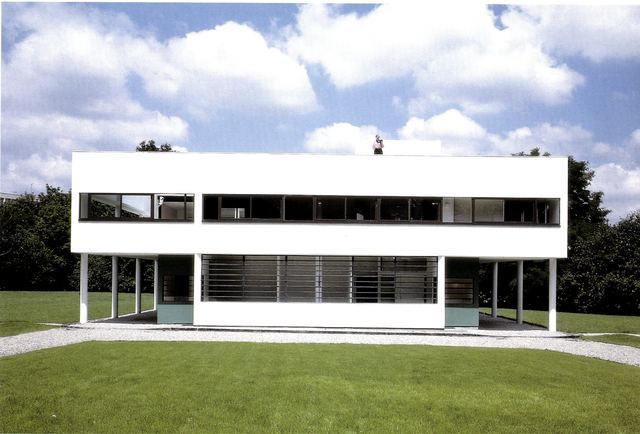
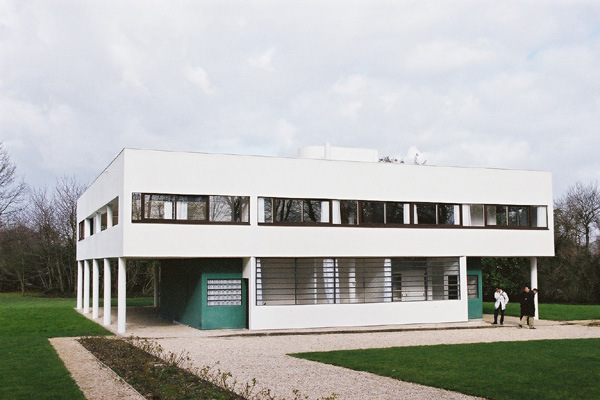
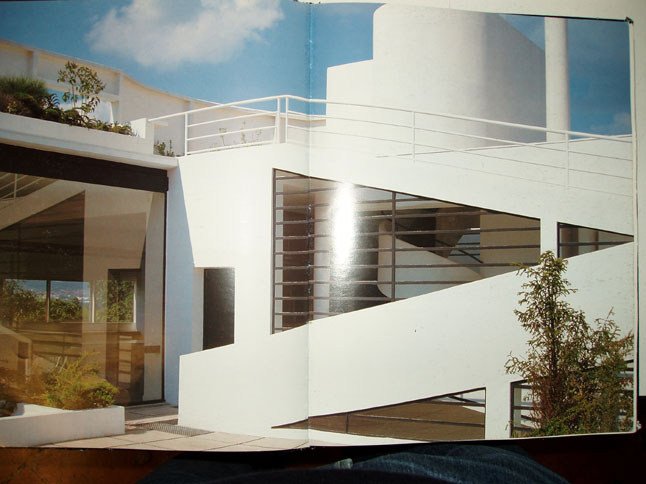
Pilotis: The villa is raised off the ground by a series of thin concrete pillars called "pilotis." This allows the building to appear to float above the ground, creating an open space beneath it.
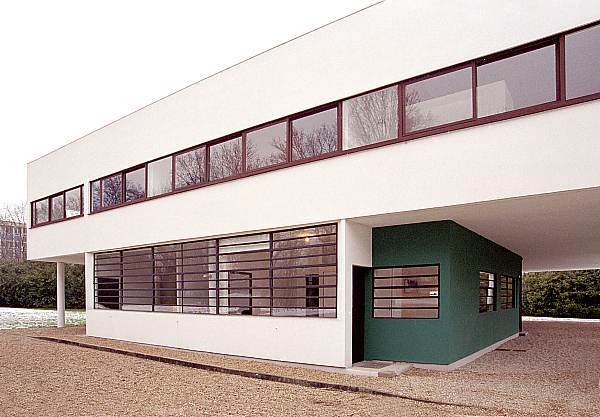
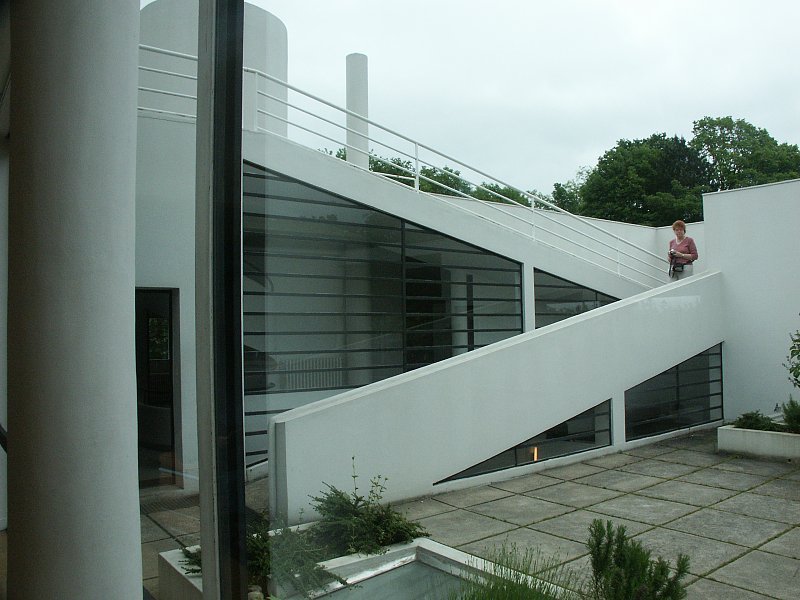
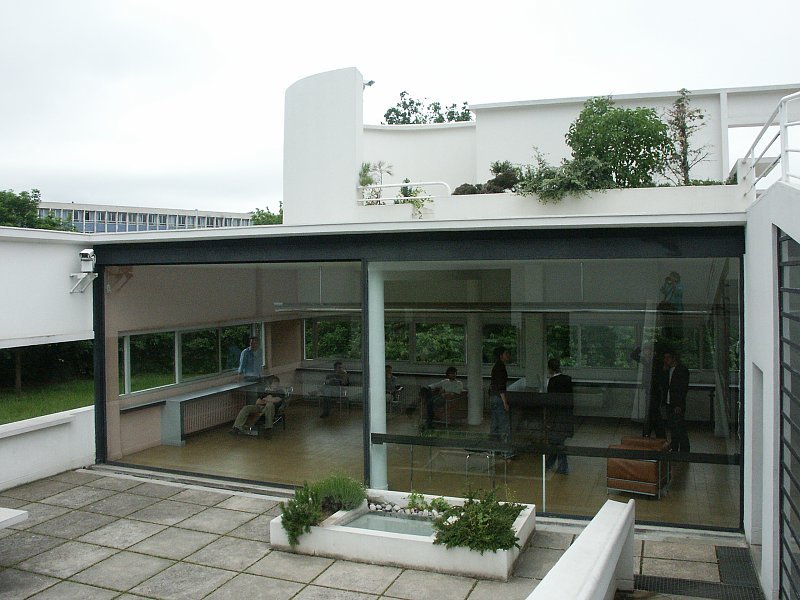
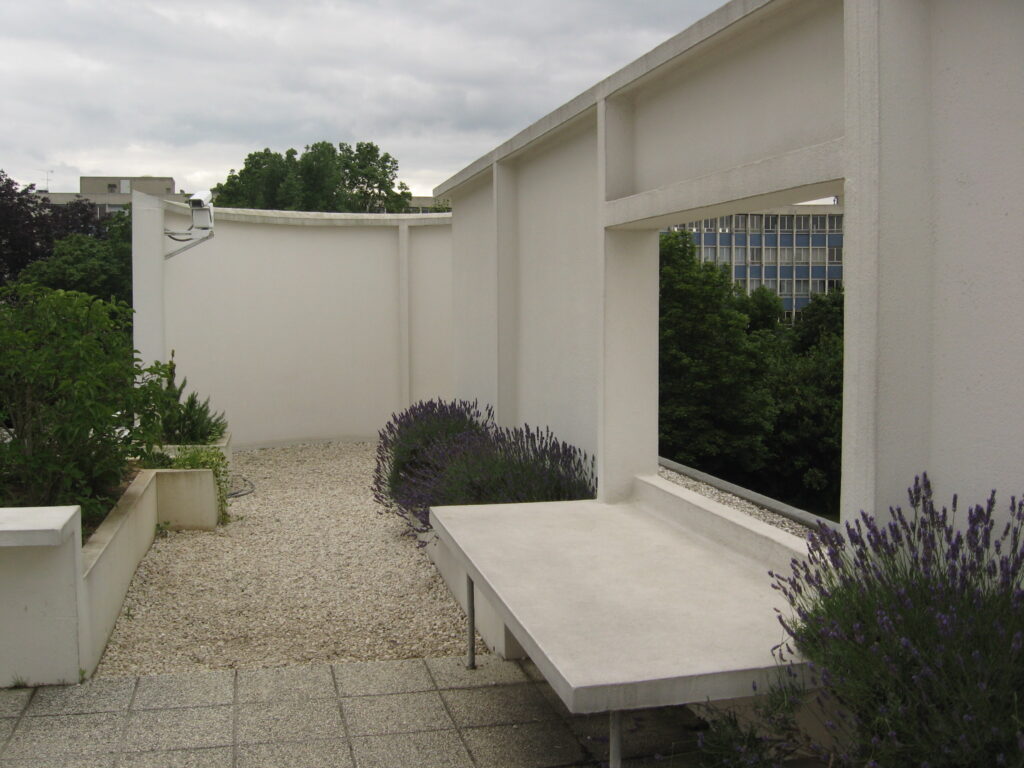
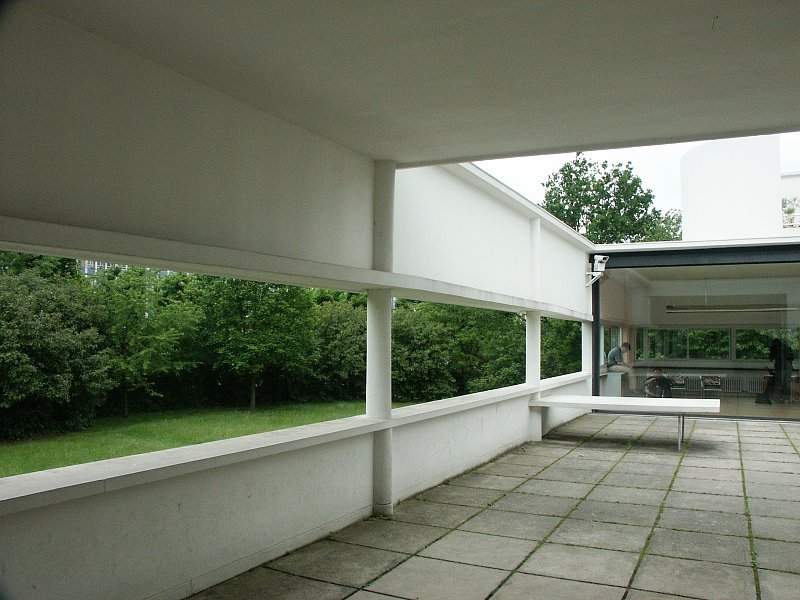
Free façade: The façade of the Villa Savoye is not a load-bearing element, which means it has been freed from structural functions. This allowed Le Corbusier to create large horizontal windows that extend along the sides of the building, giving a feeling of lightness and openness.
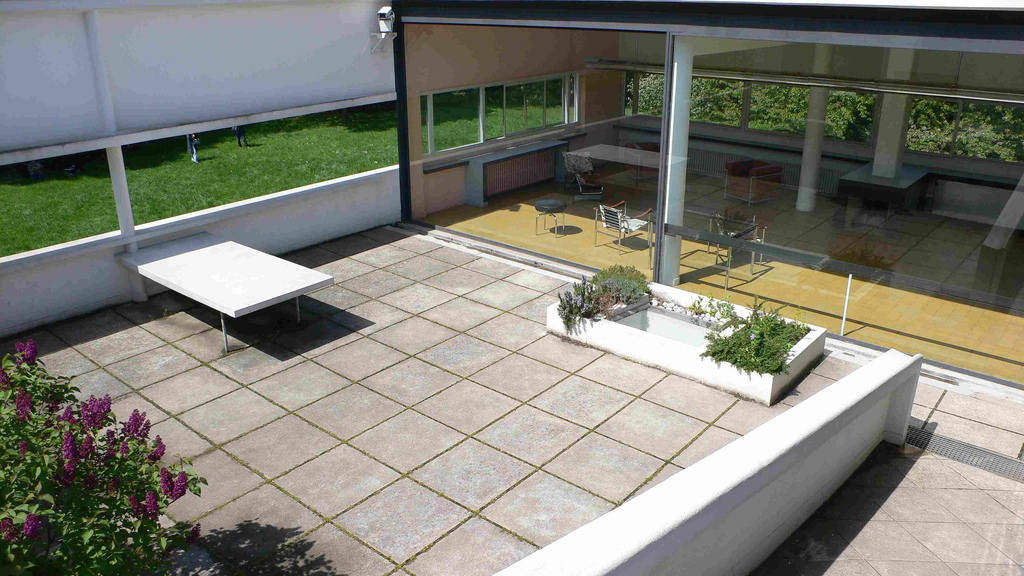
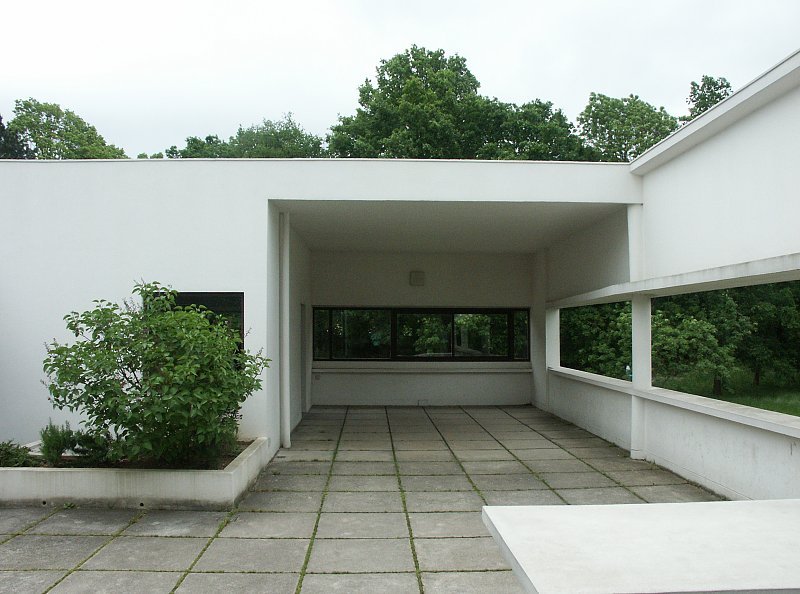
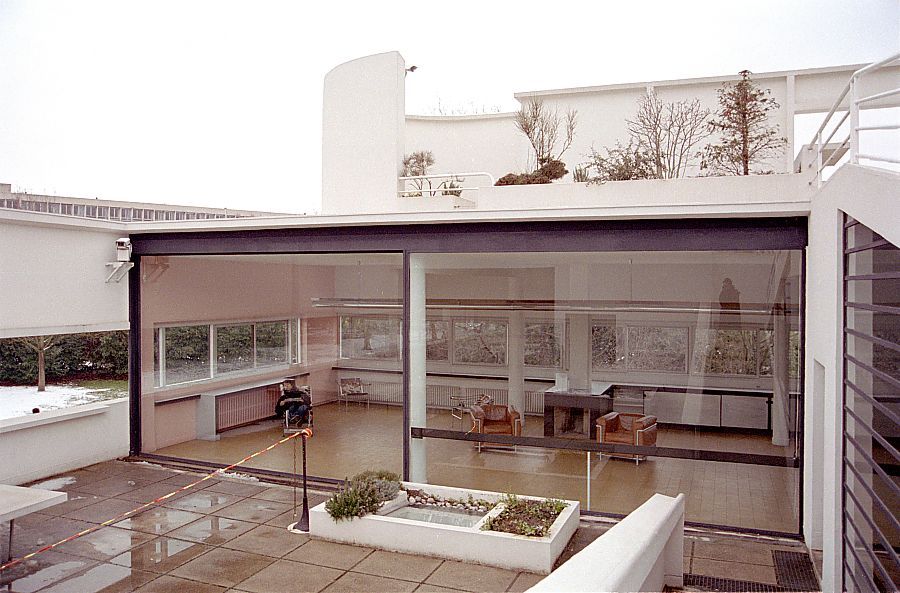
Free plan: The interior architecture of the villa is characterized by an open and flexible plan, without load-bearing walls. This allows for a more dynamic and versatile layout of interior spaces.
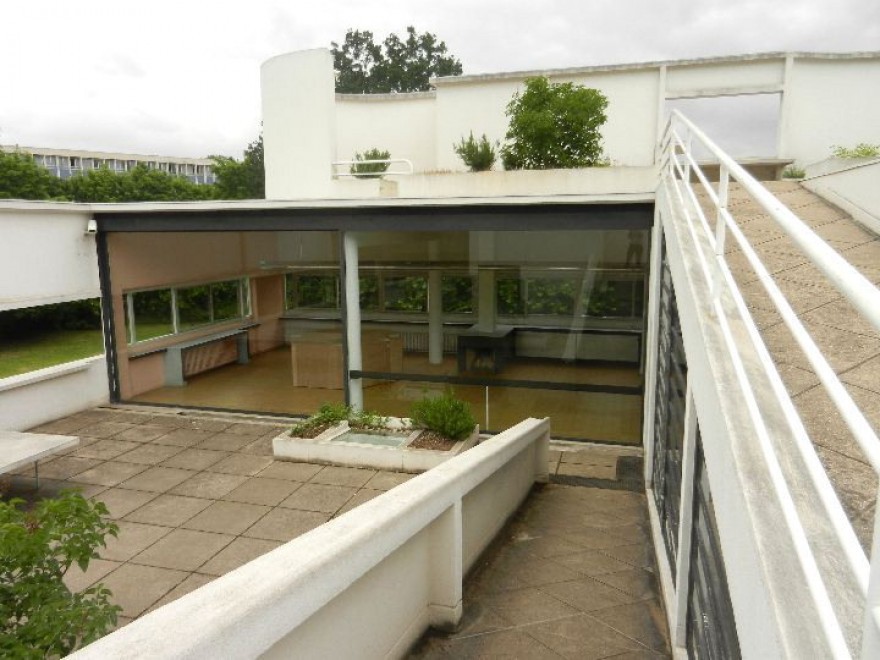
Ribbon window: Le Corbusier employed long, horizontal windows to maximize the entry of natural light into the building.
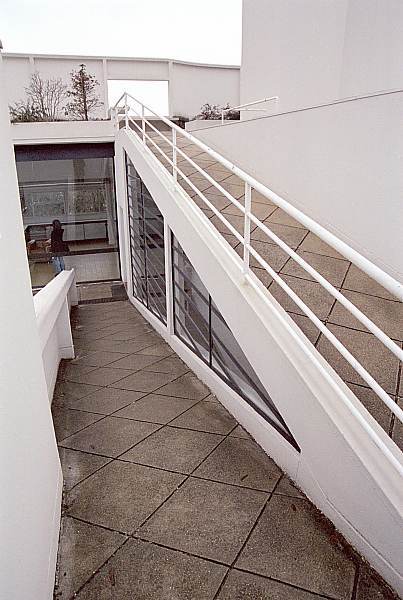
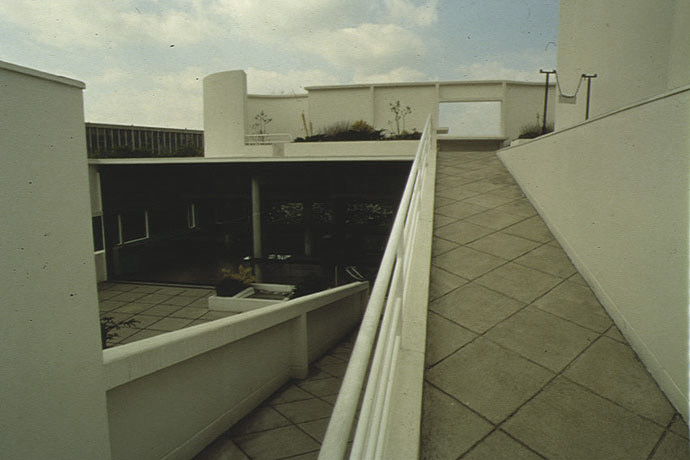
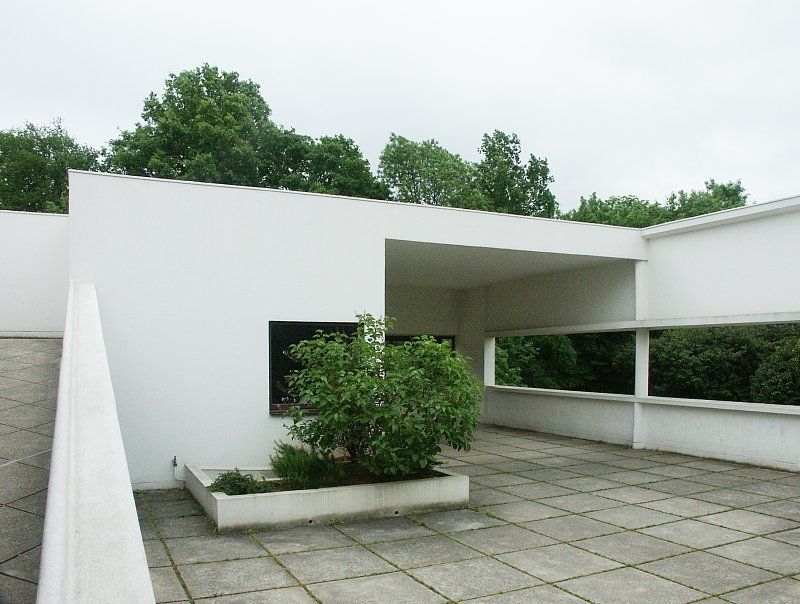
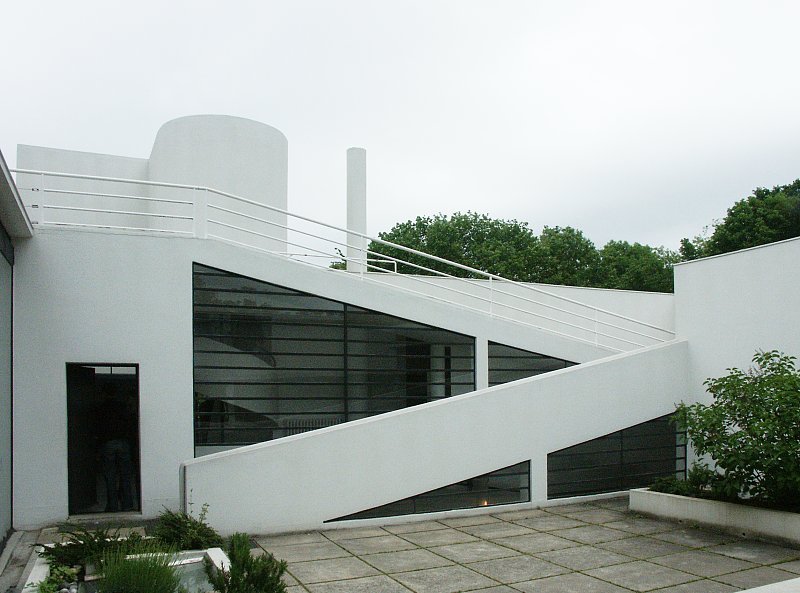
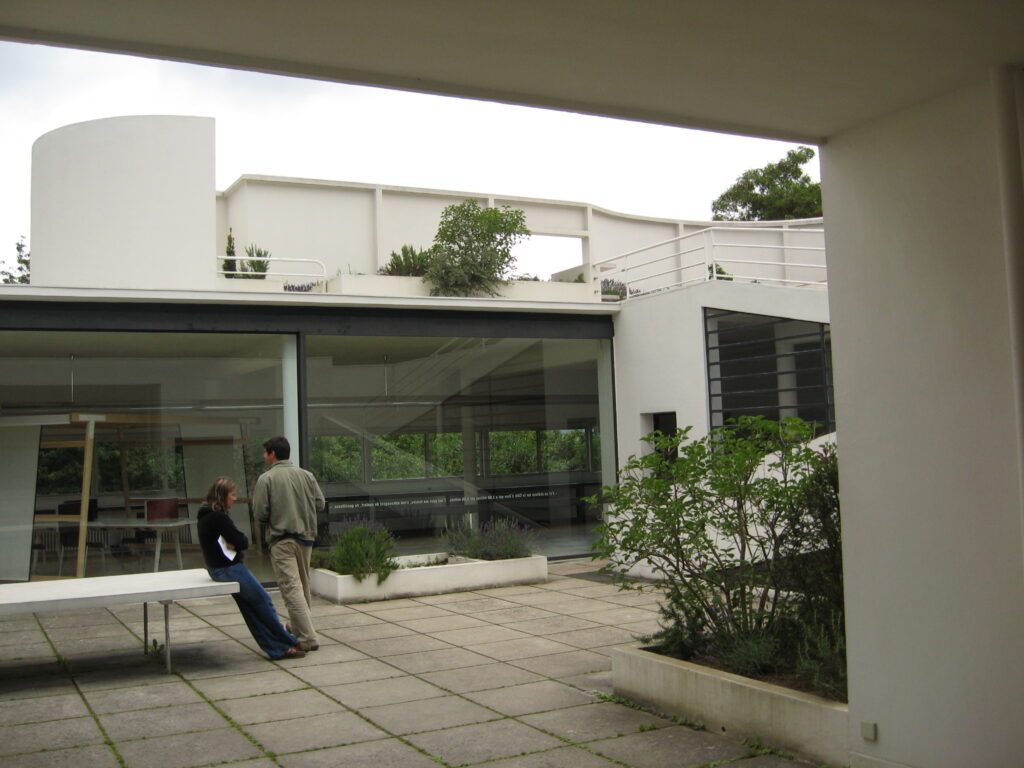
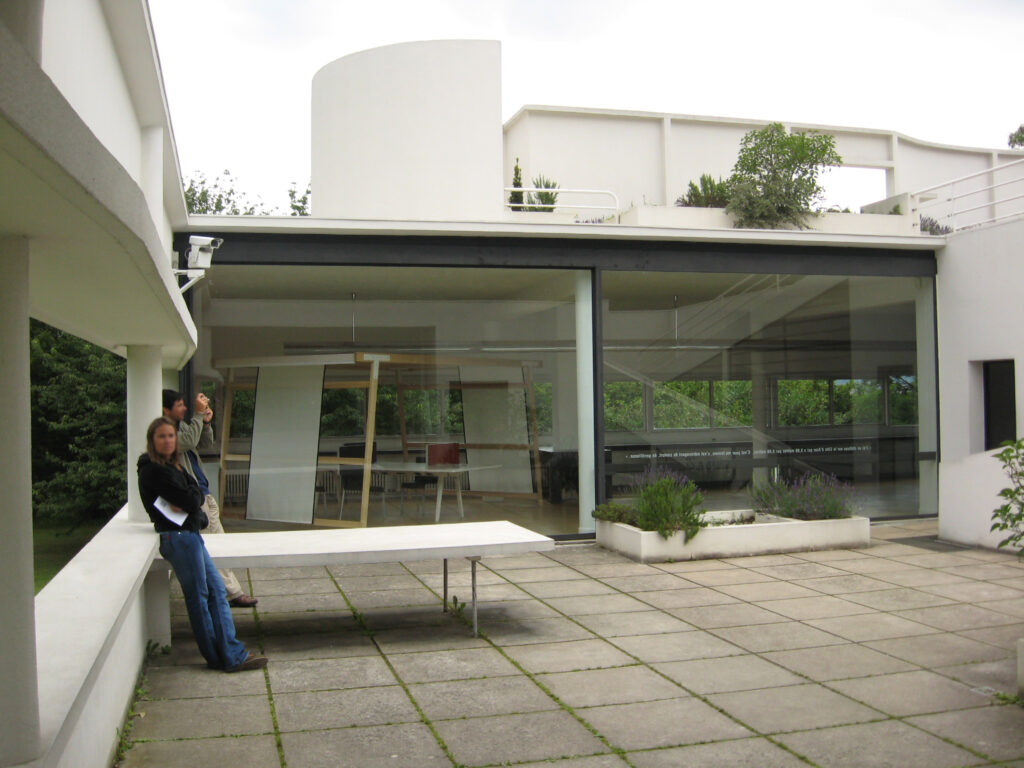
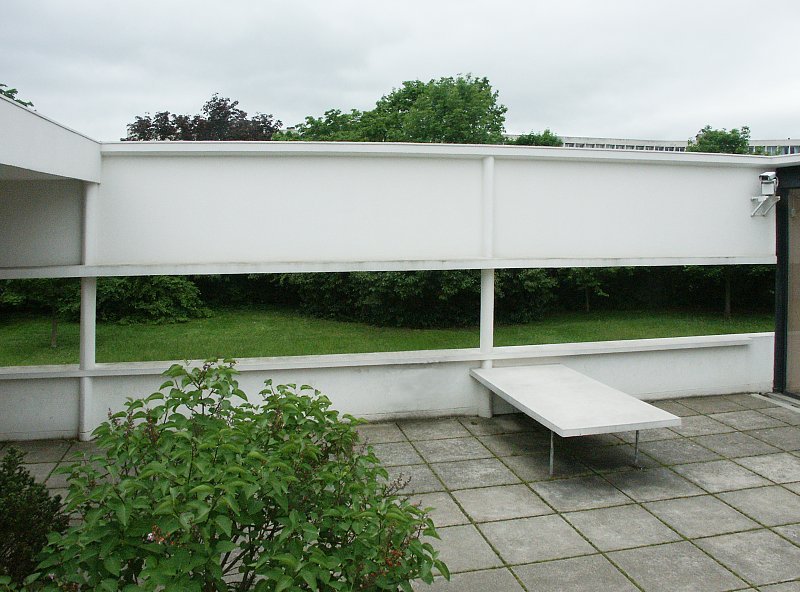
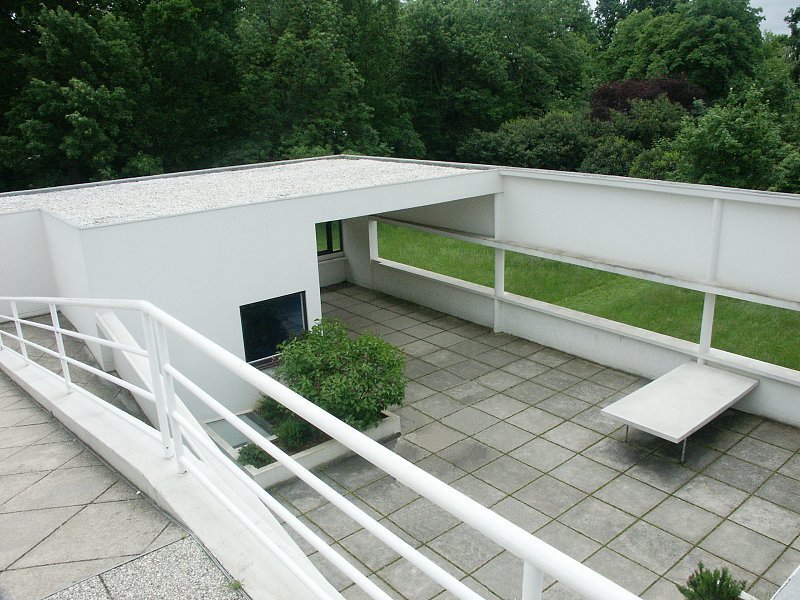
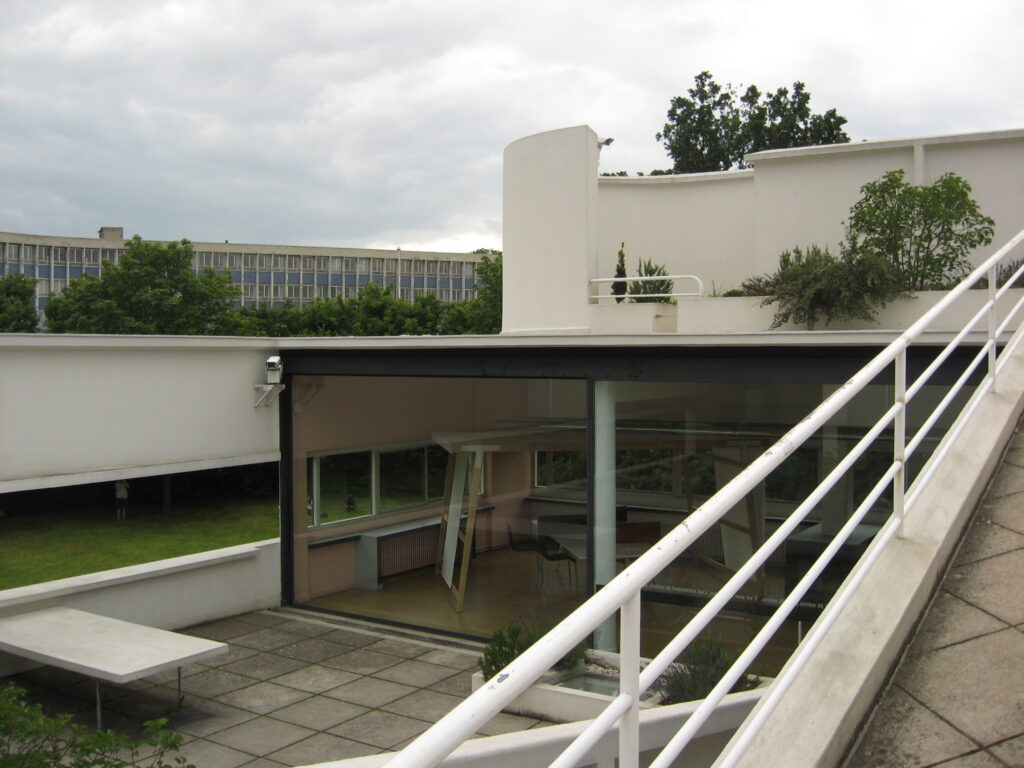
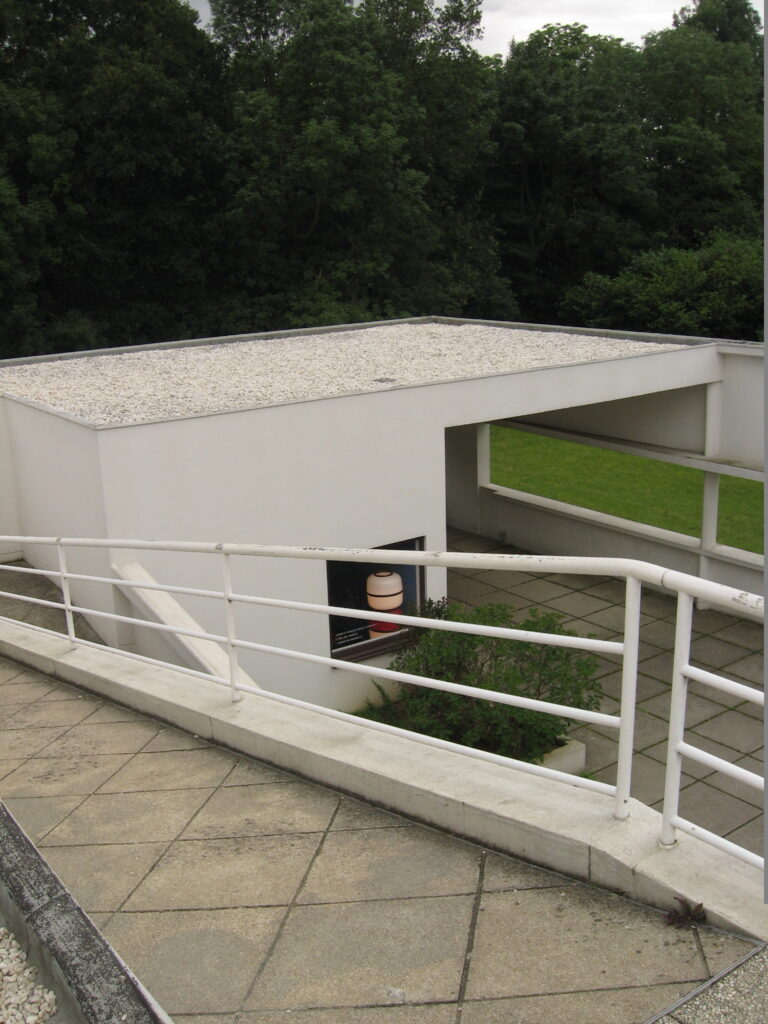
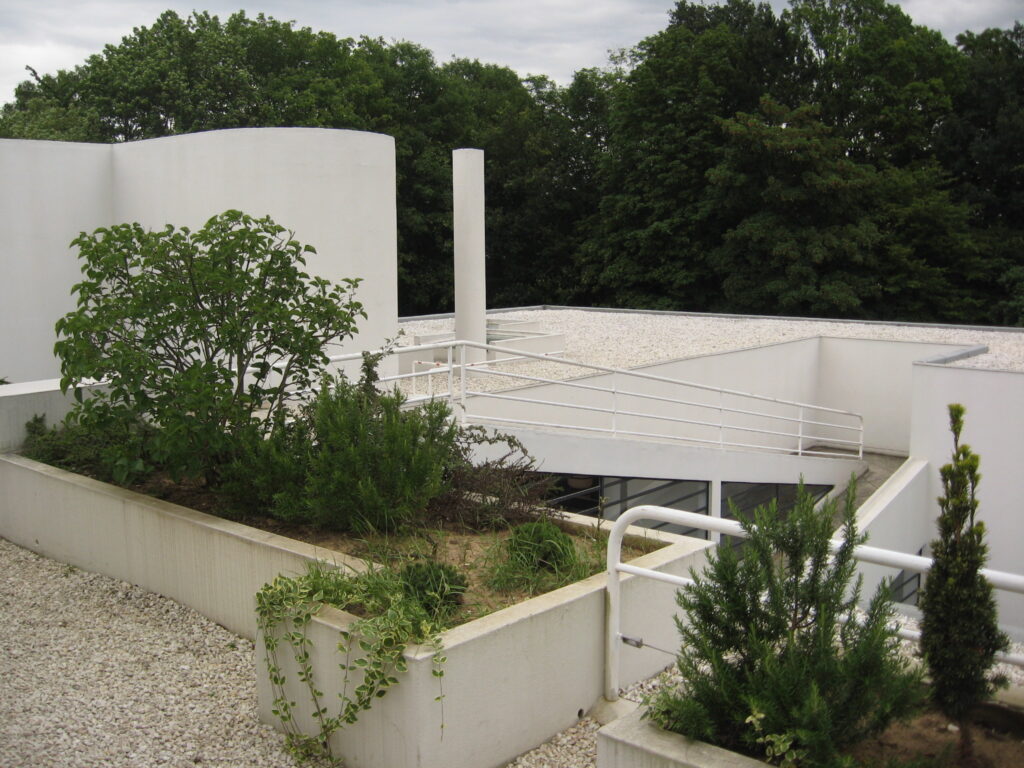
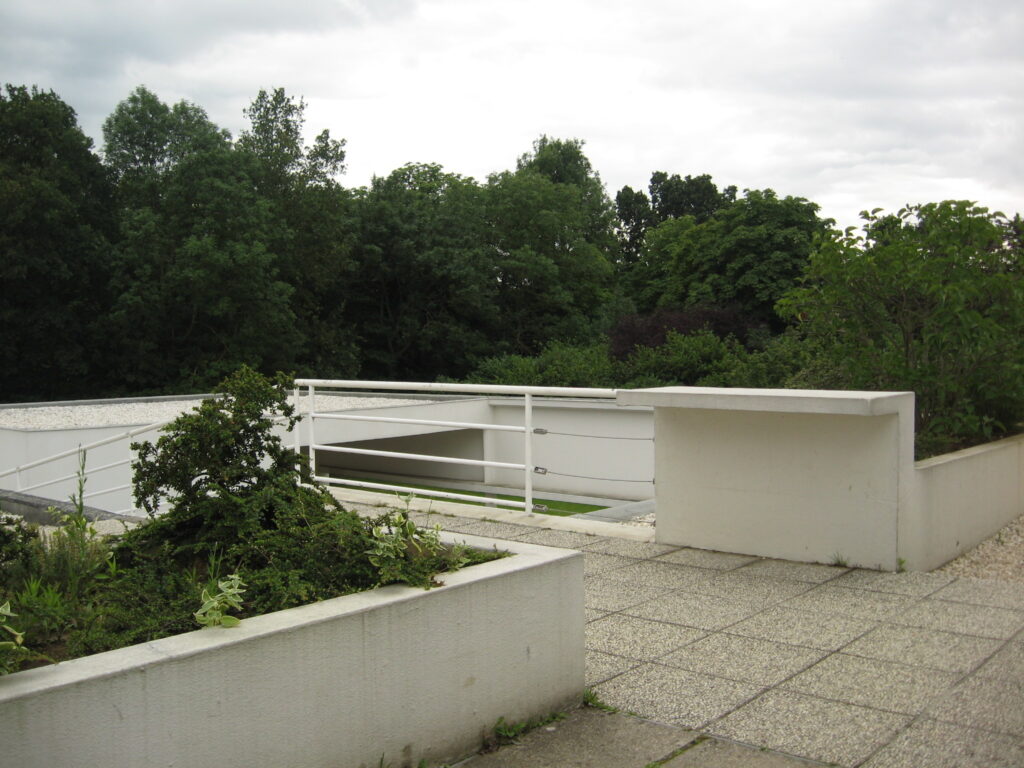
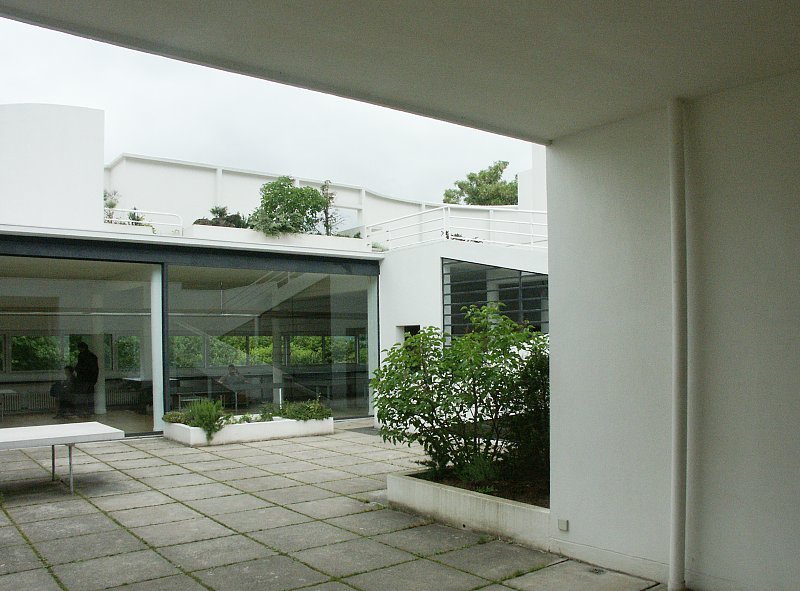
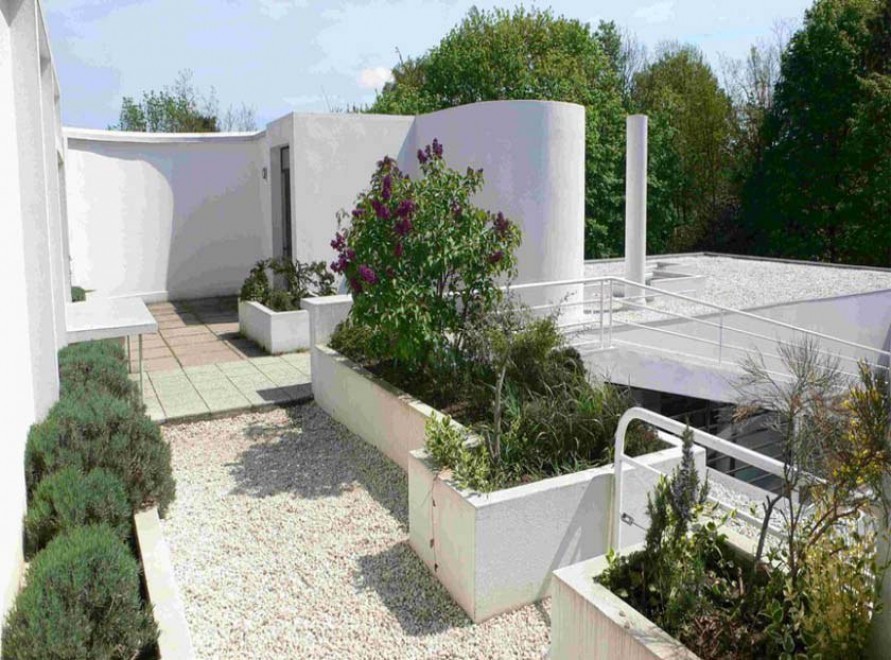
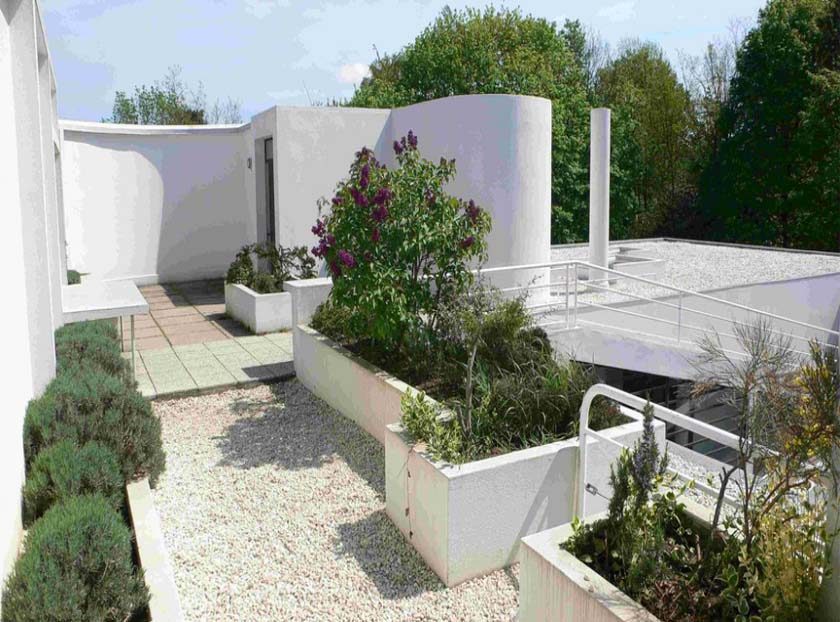
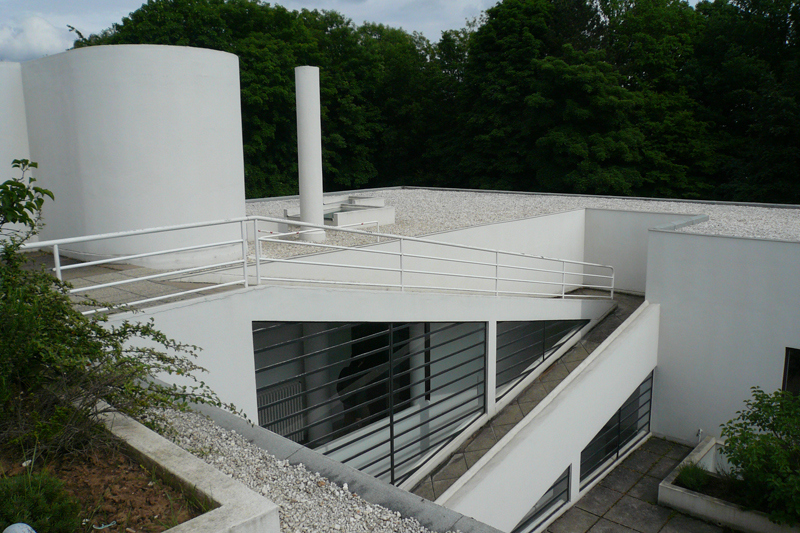
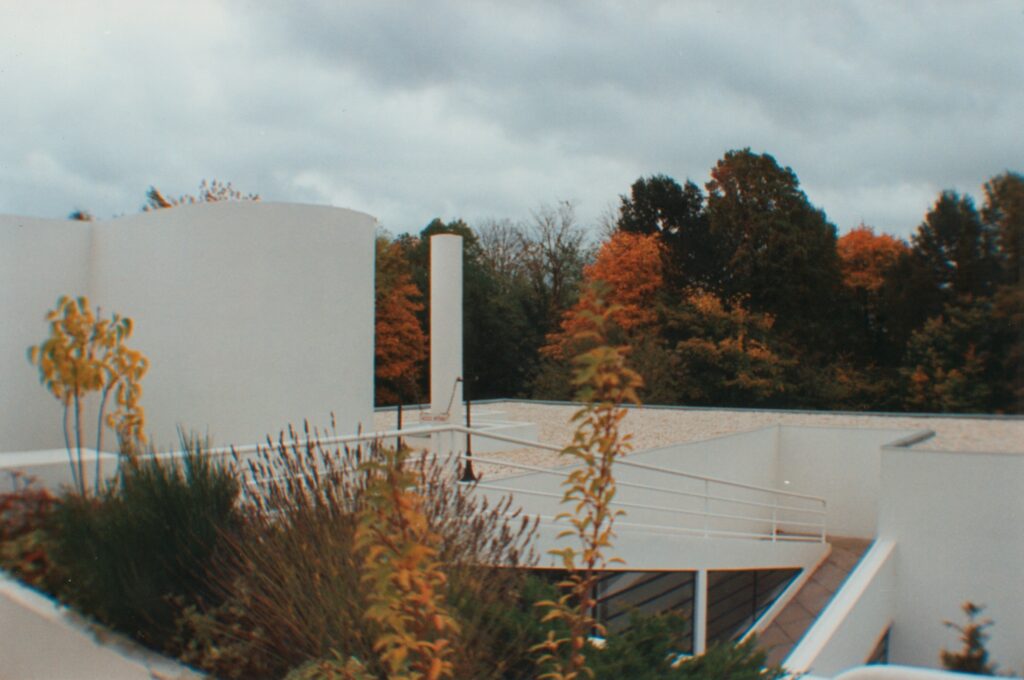
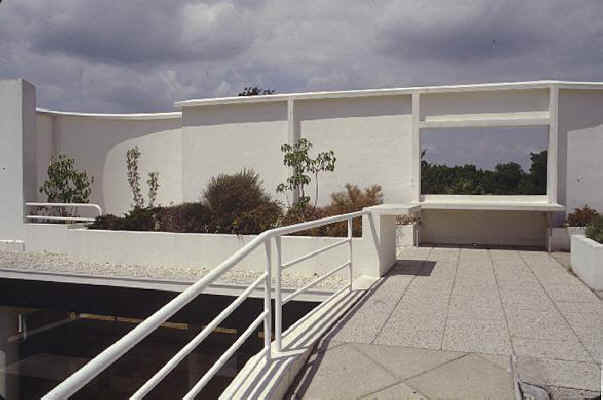
Garden terrace: The roof of the villa serves as a garden terrace, providing an outdoor space to relax and enjoy the surrounding views.
These principles have become fundamental in modern architecture and have influenced many subsequent architects.