Parking garage
Linee guida per la progettazione di un'autorimessa

Planning a garage is an undertaking that requires meticulous evaluation of numerous factors, from the size of the space to building regulations. Whether it is a single house, a condominium or a shopping centre, careful planning of the garage can make the difference between a simple parking space and a valuable space for the property.
In this article, we will explore the basic guidelines for designing a garage, addressing key aspects such as regulations, ideal dimensions, safety, flooring and drainage, lighting, ventilation and fire protection. By following these guidelines, you will be able to design a garage that is not only functional, but also safe.
What is a garage?
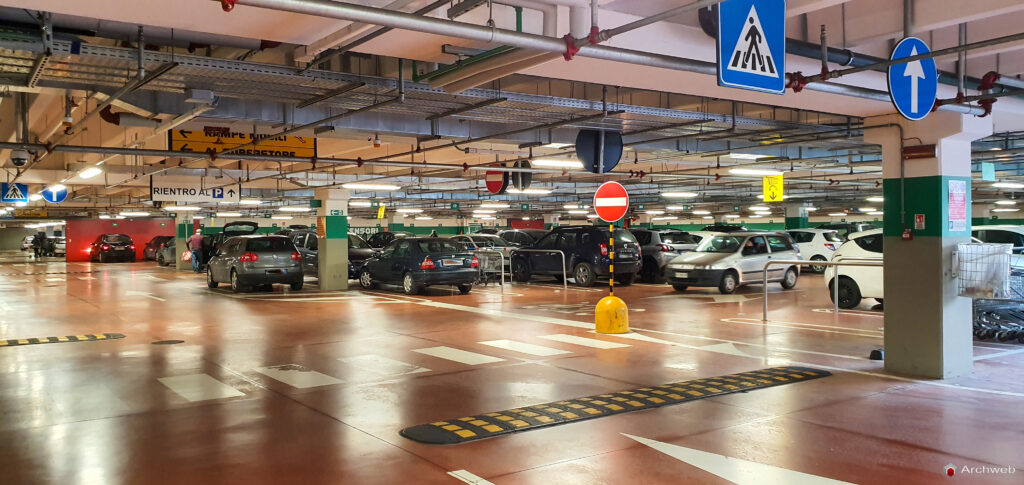
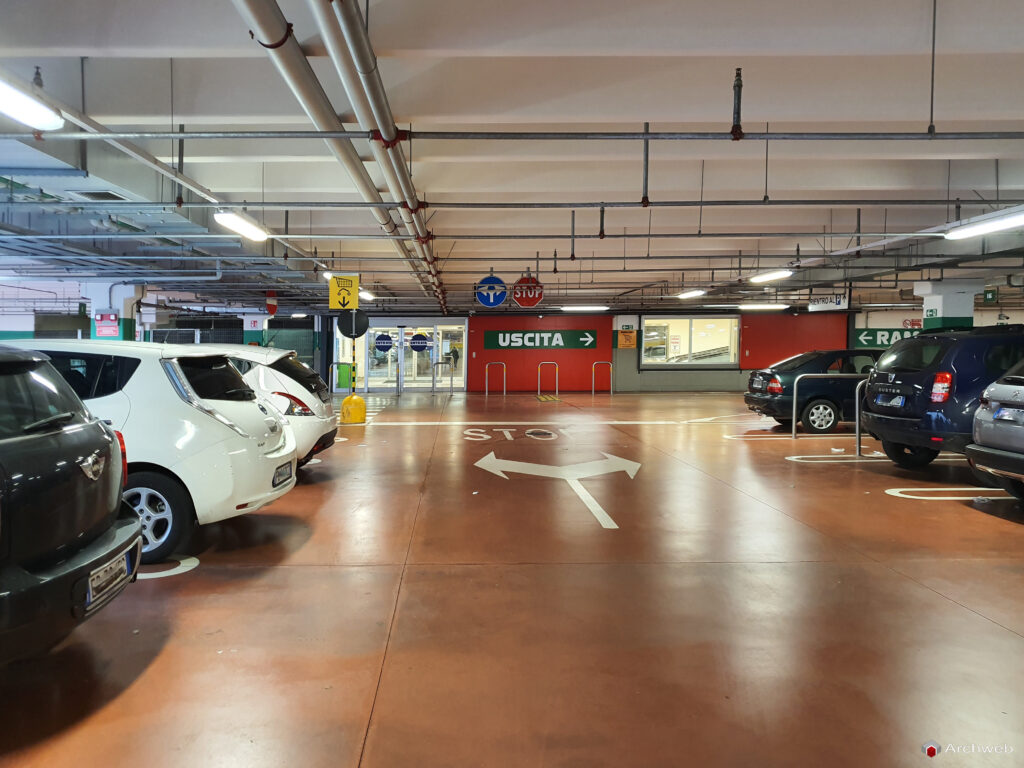
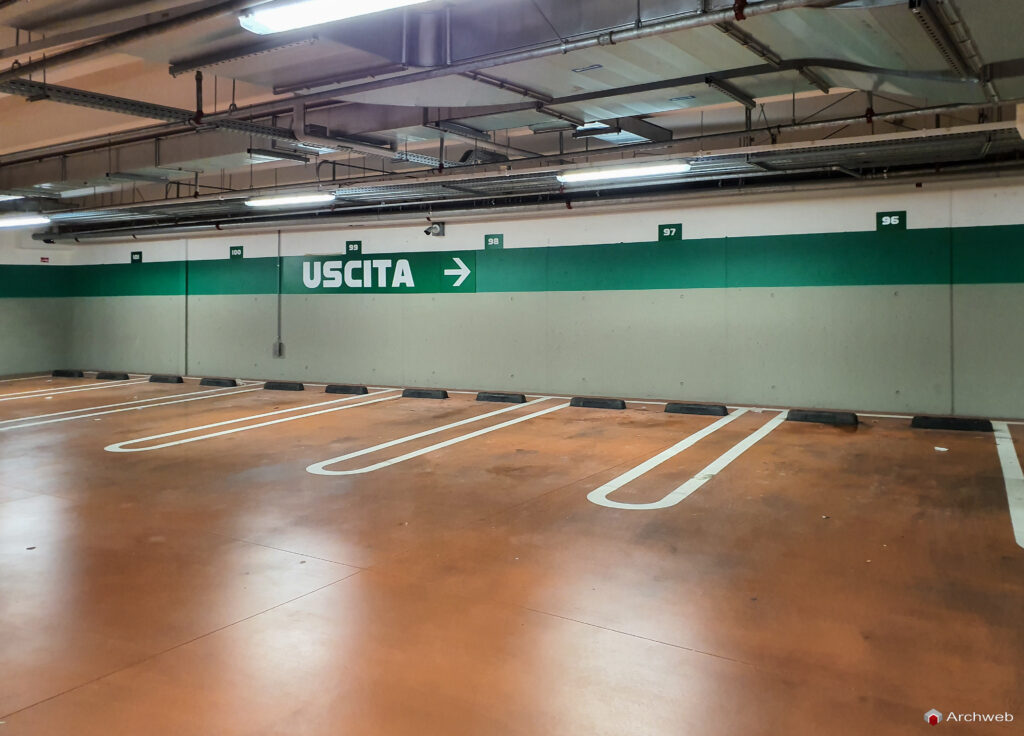
A garage is a covered and protected space, usually attached to or integrated into a residential, commercial or industrial structure, designed to house and protect one or more vehicles. Also commonly known as a garage, it can perform several functions, including:
- Safe and secure parking for vehicles.
- Storage space for equipment, tools and other goods.
- Work area for vehicle maintenance and repairs.
- Direct access to other areas of the building.
Garage design must take these different needs into account to create a functional and versatile space.
Types of garages
Based on criteria of construction, location and use, garages can be classified into different types:
- Intended use: exclusively for vehicles (isolated) or with other functions (mixed).
- Location: completely or partially underground (basement), or at ground level or above (above ground).
- Ventilation: with large openings on the perimeter for natural ventilation (open), or with limited openings (closed).
- Security: with surveillance and fire protection systems (guarded), or without specific security systems (unguarded).
- Interior organisation: with individual parking spaces (boxed) or with a single space (open space).

Importance of garage design
The careful design of a garage is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Optimisation of space: careful planning makes the best use of available space, maximising parking and storage capacity.
- Safety and security: a well-designed garage offers protection for the vehicles and goods stored inside, preventing theft and damage.
- Accessibility and traffic flow: a logical and intuitive layout facilitates the entry and exit of vehicles, improving traffic flow.
- Aesthetic integration: the garage must be designed to integrate harmoniously with the architecture of the building or its surroundings.
- Added value: careful and functional garage design can increase the overall value of the property.
Investing in the planning of a carport is an essential step to achieve an efficient, safe and well-integrated space in the building as a whole.
Reference standards for designing a garage
To design a garage according to standards, it is necessary to refer to several ministerial decrees. Ministerial Decree 21 February 2017 defines fire safety standards, while Ministerial Decree No. 236/1989 regulates parking spaces for the disabled. Ministerial Decree No. 6792/2001 provides guidance on the dimensions and layout of garages, and Ministerial Decree 3 August 2015 covers the internal division of spaces.
The Ministerial Decree of 01/02/1986, although often associated with large garages, actually applies to all premises intended for parking vehicles, including private car garages. This decree, still in force and supplemented by subsequent circulars, defines the minimum fire safety requirements. While small garages are subject to a simplified self-certification procedure, larger garages (with a total covered area of more than 300 square metres) require a more in-depth assessment by the fire brigade.
Larger garages (over 1,000 square metres) require more complex authorisation procedures, such as the submission of a fire plan and an assessment by the fire brigade. For smaller garages (up to 1,000 sqm), an SCIA is sufficient.
In addition to these national regulations, it is essential to consider any additional requirements contained in the Building Regulations of the municipality where the garage will be located.
Charging points for electric vehicles in garages
Decree Law 257/2016 introduced the obligation to prepare newly constructed or renovated buildings for the installation of electric vehicle charging points. This legislation applies to both residential buildings with at least 10 residential units and non-residential buildings with an area of more than 500 square metres. The aim is to encourage the spread of sustainable mobility and facilitate the charging of electric cars in car parks.
Guidelines for designing a garage
Here are the main guidelines to follow when designing a garage:
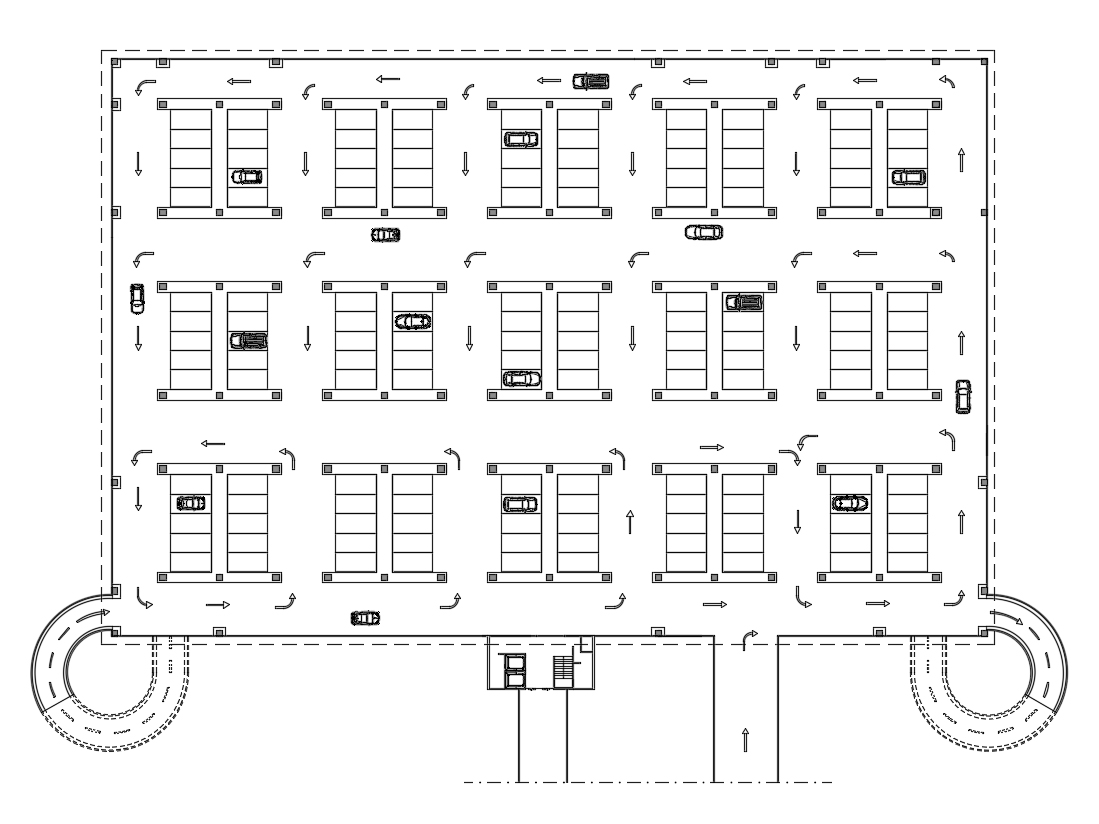
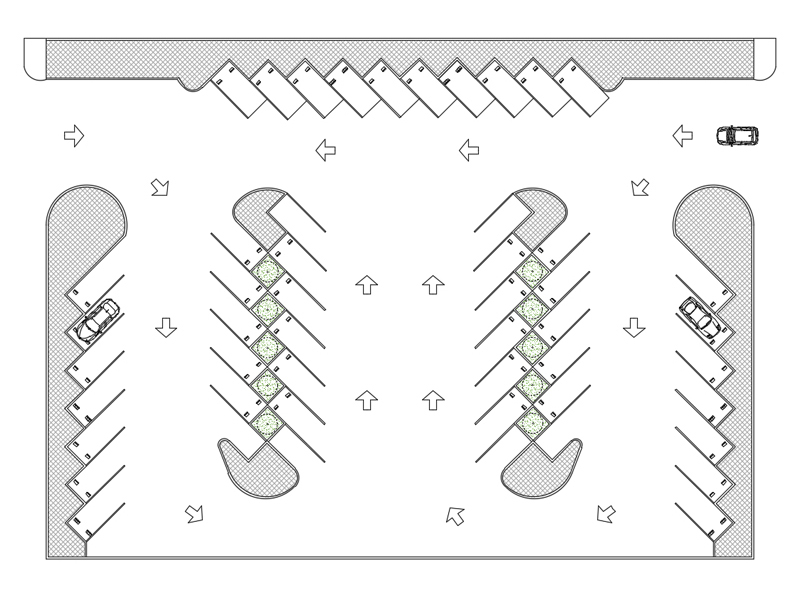
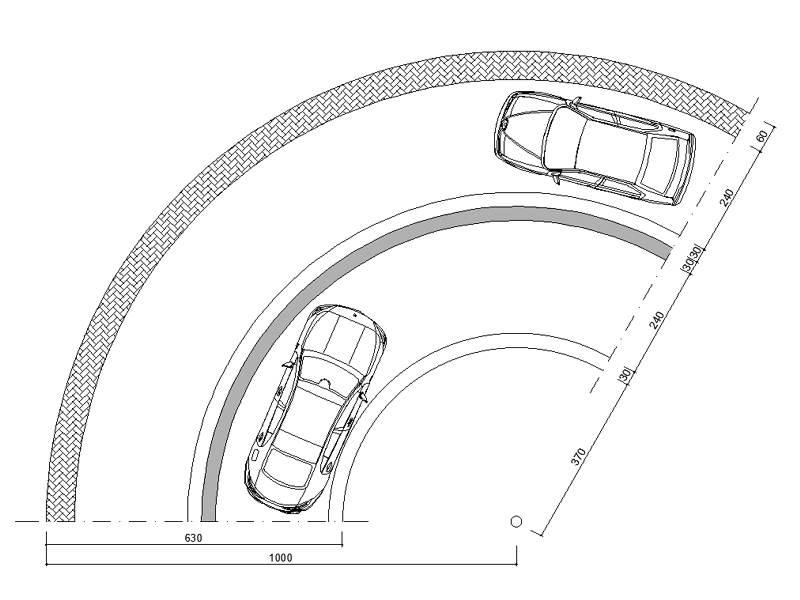
Ideal size and layout for a garage
The dimensions of the garage must be adapted to the specific requirements. As a general rule, a space of at least 2.5 by 5 metres is recommended for a single-car garage, to be increased to at least 3.2 by 5 metres if access for persons with reduced mobility is planned.
The layout of the garage must be carefully studied to optimise the organisation of the space. Some effective solutions include:
- Separation of parking and storage/work areas.
- Inclusion of accessory spaces such as storage rooms or work areas.
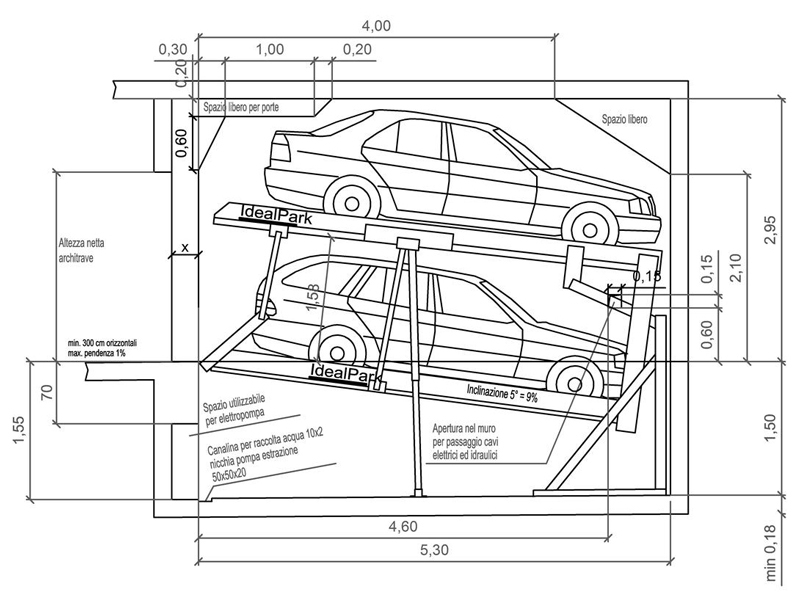
2. Garage materials and structure
The choice of materials for garage construction is crucial to ensure its strength, durability and resistance. Some common materials include:
- Reinforced concrete or steel structure for solidity.
- Walls of brick, concrete blocks or prefabricated panels.
- Roofing in tiles, sheet metal or bricks.
The garage structure must be designed to withstand the weight of the vehicles, the stresses caused by opening and closing the doors, and any environmental stresses.
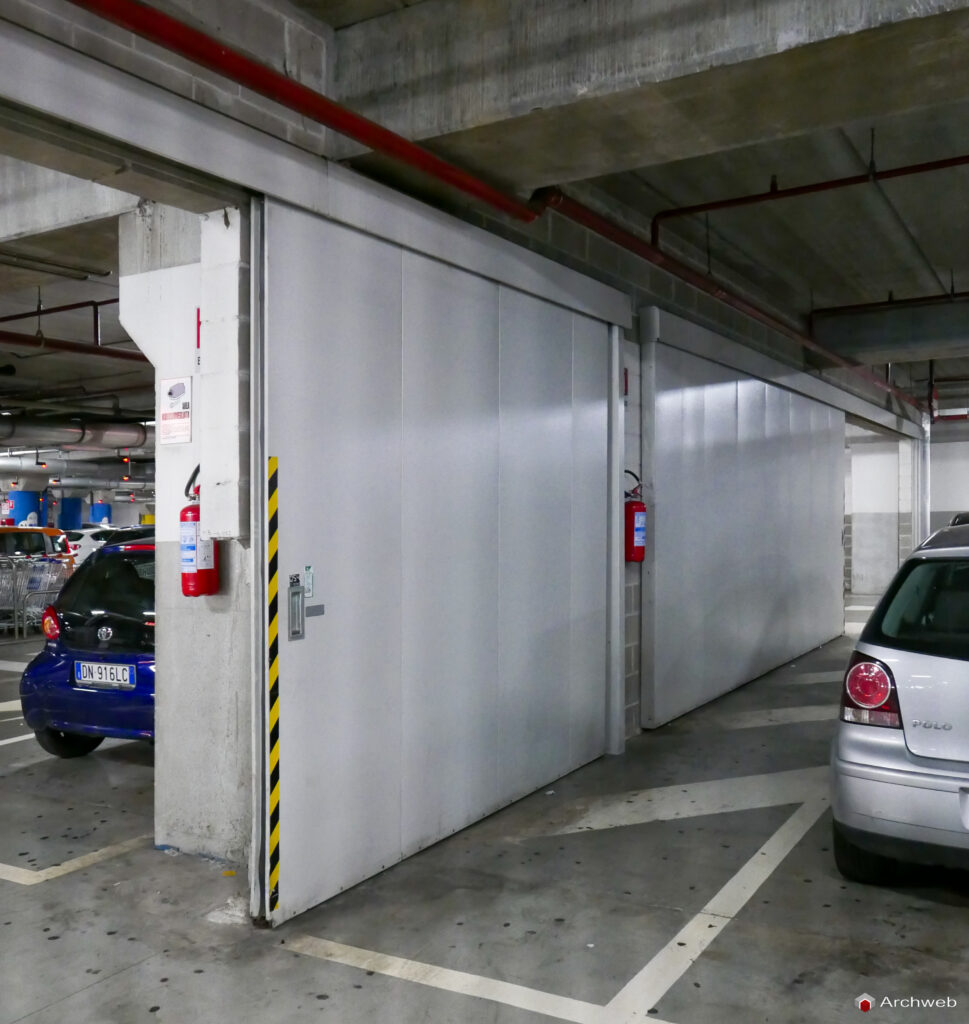
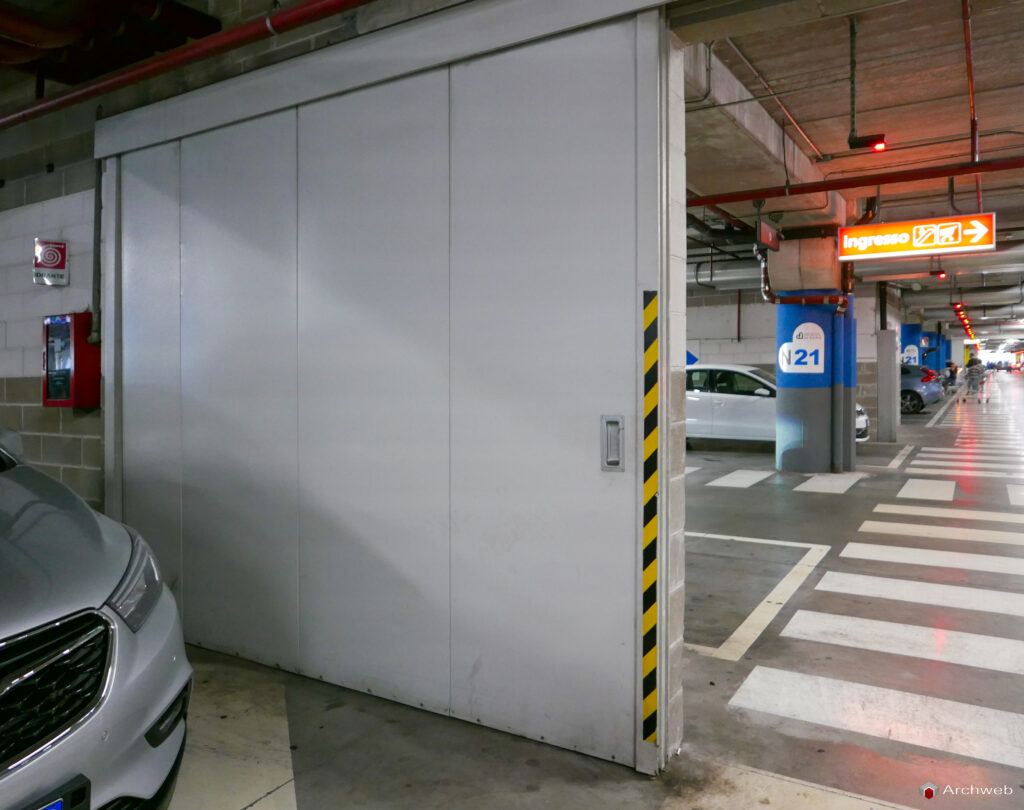
Security and garage locking system
Garage security is a crucial aspect. Some solutions to ensure protection include:
- Fire-retardant entrance/exit doors with security locks.
- Appropriate lighting systems for the entire garage area.
- Surveillance cameras and motion sensors, if necessary.
- Possible installation of an intruder alarm system.
The garage locking system must be reliable and easy to use, allowing access only to authorised persons.
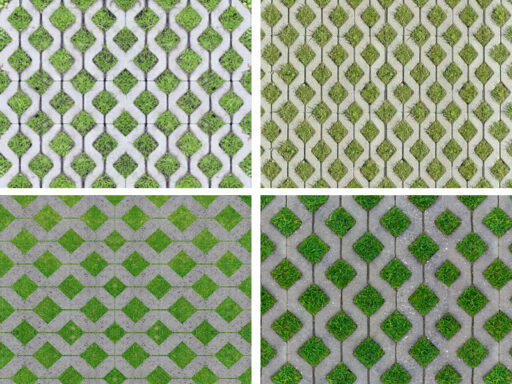
4. Garage paving and drainage
The choice of garage flooring must consider factors such as strength, ease of maintenance and aesthetic appearance. Some common options are:
- Concrete or industrial flooring.
- Non-slip tiles or slabs in resistant materials.
- Draining solutions to facilitate water drainage.
A proper drainage system is essential to avoid water stagnation and to keep the garage dry and clean.

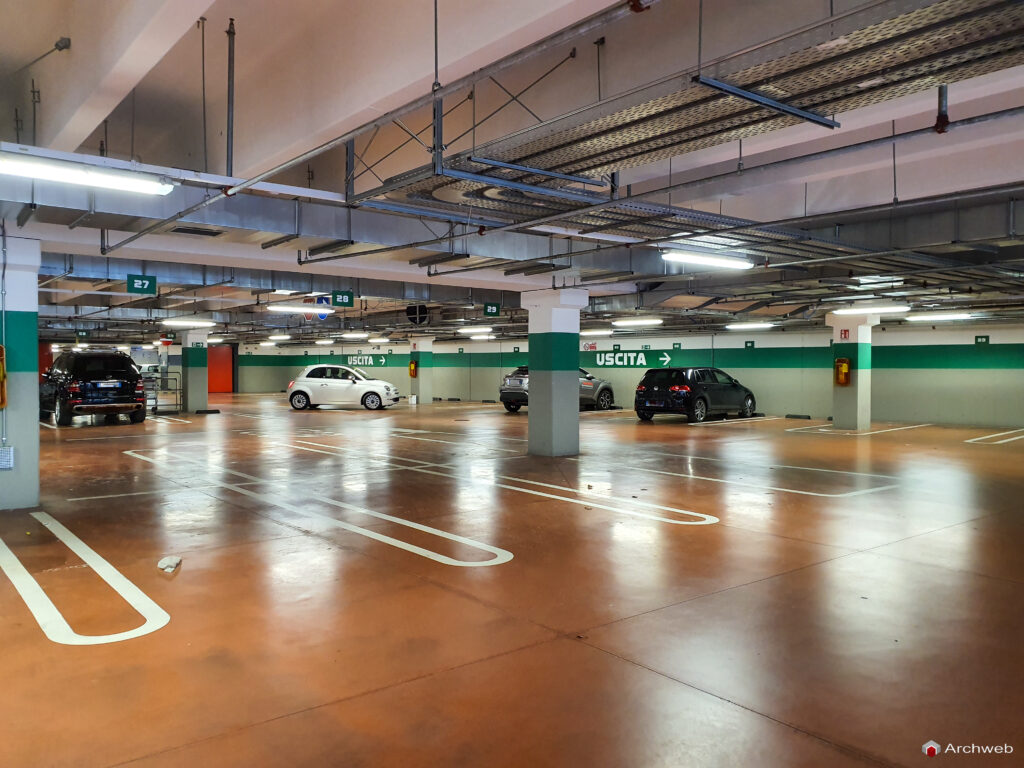
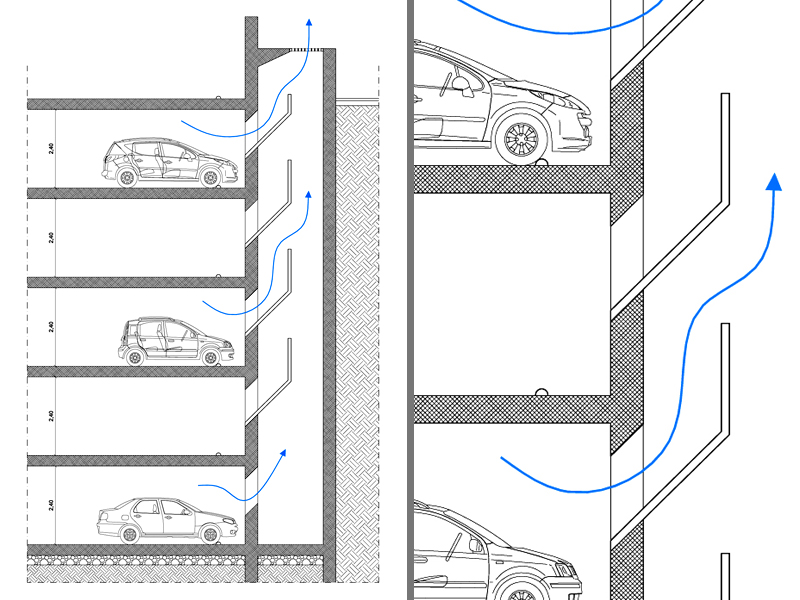
5. Garage lighting and ventilation
Adequate lighting and effective ventilation are essential for the functionality and comfort of the garage. Some guidelines:
- Sufficient lighting to ensure visibility and safety.
- Use of LED lamps or other energy-efficient solutions.
- Natural or mechanical ventilation to ensure adequate air exchange.
Good lighting and ventilation contribute to a pleasant and healthy working environment.
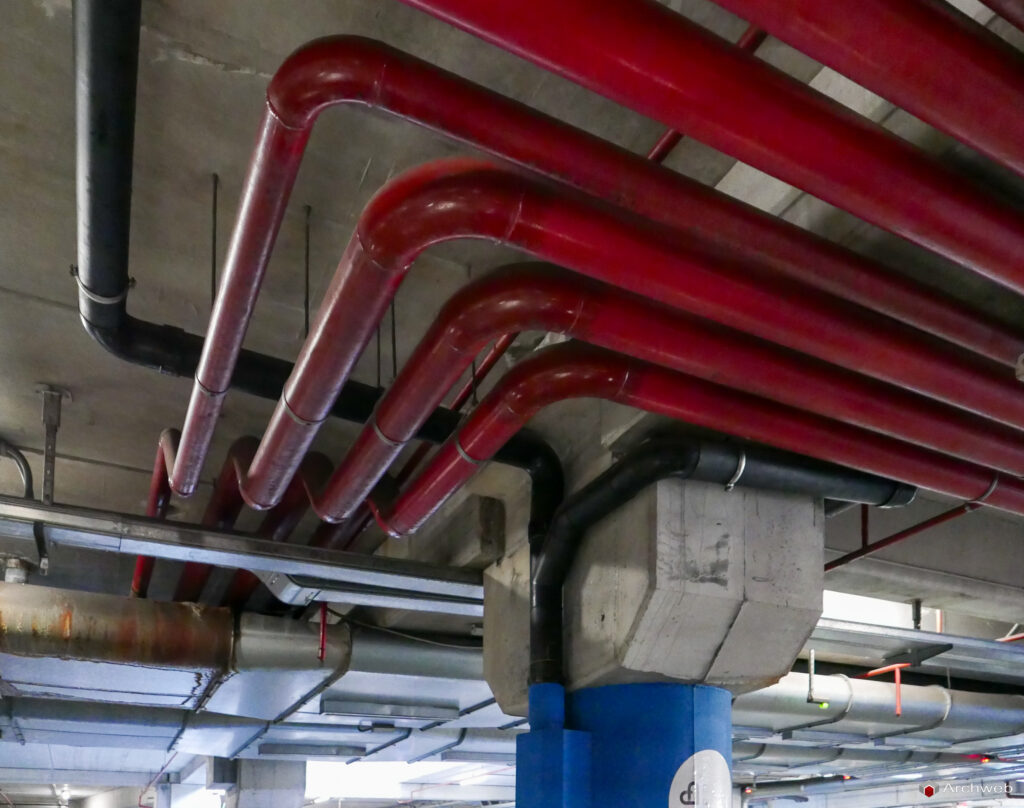
6. Fire-fighting system
When designing the garage, special attention must be paid to the prevention and management of fire risks. Some fire safety measures to consider are:
- Installation of fire extinguishers and/or an automatic detection and extinguishing system.
- Provision of escape routes and emergency signs.
- Compliance with applicable fire regulations.
These precautions help to ensure the safety of all garage users.
Conclusions
Designing a garage is a complex process that requires careful planning to meet parking requirements.
The guidelines presented in this article can help you in designing a garage that not only complies with current regulations, but is also functional and safe.