The photovoltaic facade
Technology for sustainable architecture

Sustainable architecture aims to design buildings with low environmental impact.
A low environmental impact building is a building designed to promote sustainability throughout the life cycle: from design to demolition to recycling of materials.
Furthermore, the eco-sustainable building pays maximum attention to the concept of energy efficiency. Elements such as the photovoltaic facade represent one of the many solutions currently achievable.
Eco-sustainable design
Eco-sustainable design has key points to respect to limit the environmental impact of buildings, achieve energy efficiency, minimize the use of available resources without neglecting living comfort and design.
Buildings are responsible for approximately 60% of national energy consumption. Greater energy consumption means greater consumption of resources and emissions into the atmosphere. This is why reducing emissions is essential and exploiting renewable energy is vital!
Key points of eco-sustainable design
To design in an eco-sustainable way, key points of considerable importance must be respected:
- orientation of the building: important to ensure maximum use of solar hours and therefore avoid resorting to artificial lighting and, at the same time, a well-oriented building increases the individual’s living well-being;
- energy efficiency: a building has good energy efficiency if it adopts solutions and technologies capable of minimizing energy consumption for its daily energy needs;
- sustainable materials: choose materials that have a low environmental impact, which are recyclable and not harmful to humans and the environment;
- renewable energy sources: renewable energies are all those that derive from natural resources and are constantly generated according to natural cycles.
Among the various sources of renewable energy, solar energy is certainly the main source of energy for life on Earth.
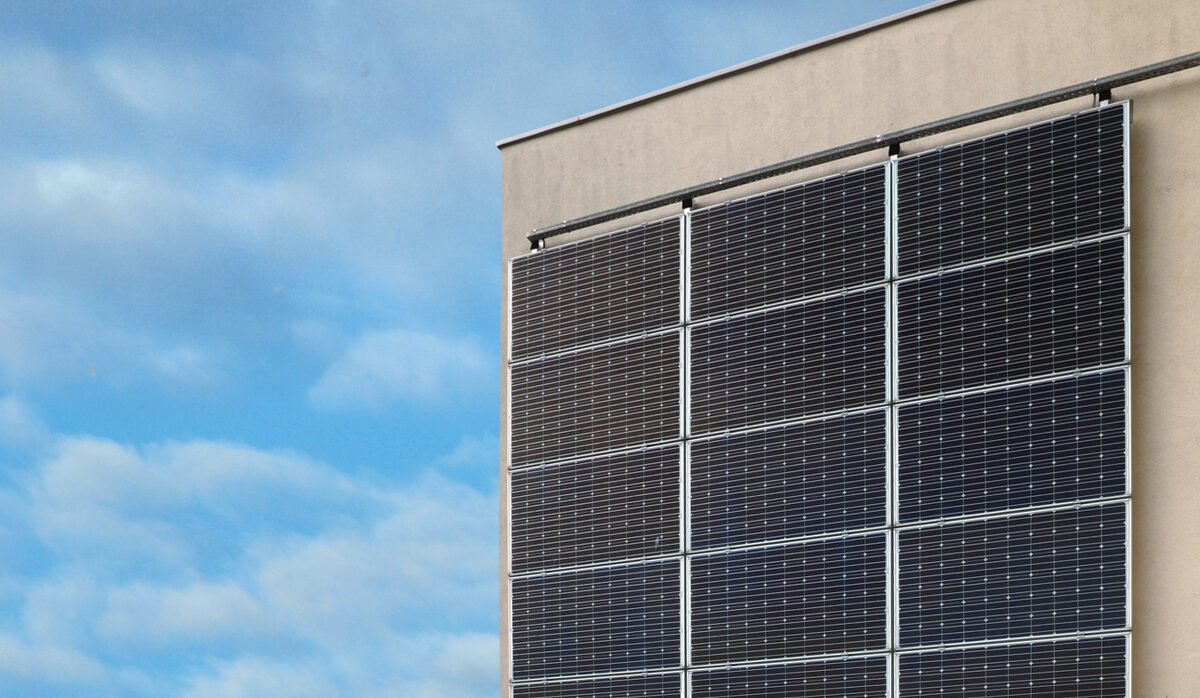
The photovoltaic facade
Photovoltaics allows you to exploit solar energy to produce electricity in a sustainable way.
Generally when we talk about photovoltaic systems, we immediately think of a system positioned on the roof of homes. Although these types of systems are the most widespread solution, they do not represent the only alternative. In fact, photovoltaic facades are becoming increasingly widespread.

Photo: Maxshot on Depositphotos.com

Photo: jarp14 on Depositphotos.com
What is the photovoltaic facade
The photovoltaic facade is the winning combination of architecture and technology for the production of renewable energy.
Covering the façade of a building with photovoltaic panels means having and making available a receiving surface that is far greater than the surface of the roof, and will therefore allow the production of greater renewable energy.
Types of photovoltaic facade
Technically we can distinguish two installation systems:
- BAPV (Building Attached Photovoltaic)
- BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaic)
The BAPV system consists of installing photovoltaics on existing surfaces. It is generally used in energy requalification projects.
In this case the photovoltaic panels are part of the building but do not replace the materials or architectural components that compose it.
The BIPV system, on the other hand, consists of replacing where the installation is planned, the architectural element (examples are photovoltaic windows and photovoltaic roof tiles).
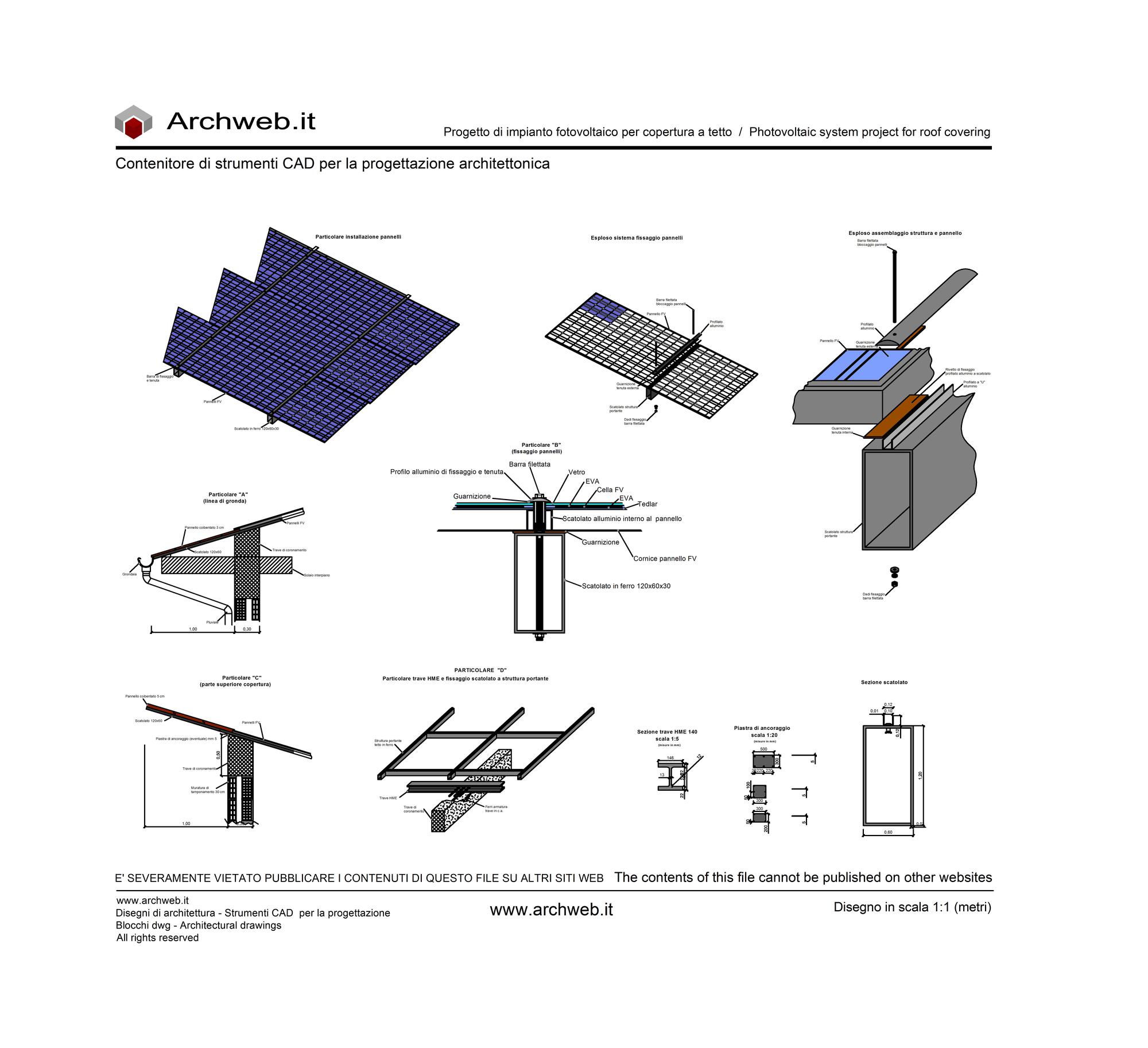
Installation of the photovoltaic facade
Photovoltaic facades require careful design for optimal results in terms of energy efficiency.
During the design phase it is good to evaluate:
- solar exposure: the facades facing south-east and south-west are certainly the best because they receive the greatest amount of daily sunlight;
- the surrounding situation: evaluate possible shading due to nearby buildings or other obstacles that may prevent direct radiation on the facade;
- correct choice of system: it is necessary to evaluate the climatic characteristics of the place to choose the most suitable photovoltaic system.
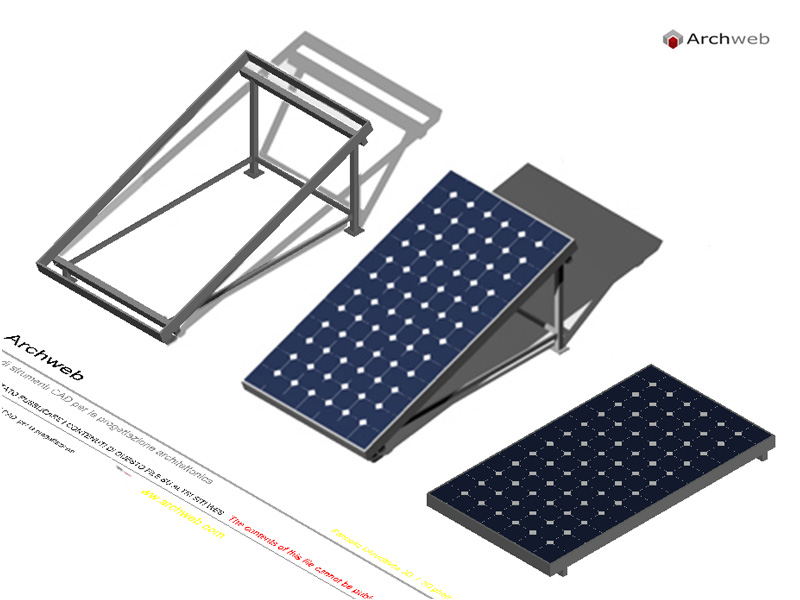
Types of panels for photovoltaic facade systems
There are different types of photovoltaic panels for facades on the market. The choice will be guided not only by the right design, but also by aesthetic taste.
In particular we can distinguish:
- polycrystalline silicon modules;
- thin film modules;
- flexible photovoltaic panels;
- photovoltaic ventilated facades.
Polycrystalline silicon modules are more efficient. However, due to their aesthetic appearance, they are not always chosen to be installed on building facades.
Thin film models are the most flexible. Although they are less efficient than polycrystalline silicon modules, they are often used in facades because thanks to their flexibility it is possible to cover even irregular surfaces.
Flexible photovoltaic panels are an evolution of thin film models. In fact they are even thinner, flexible and lighter.
Photovoltaic ventilated facades are composed of panels with thin film technology instead of window glass.
The system must be in harmony with the building, in addition to functionality it must guarantee aesthetic value and design.

The integrated photovoltaic facade
The European Community develops environmental sustainability plans, proposing directives that can develop design solutions integrated with photovoltaic technologies. Modern architecture therefore seeks to reconcile aesthetics and ecology.
In the most technological cities, imposing photovoltaic facades make their appearance.
The Lausanne Polytechnic School, for example, was the first to use a glass façade system composed of dye-sensitized photovoltaics.
These cells, invented in 1991 by prof. Michael Gratzel, are able to produce the principles of photosynthesis in plants and produce energy regardless of the angle of solar incidence.
Another example is the Hanwha Headquarters in Seoul, where the facades feature a system of panels and windows arranged in such a way as to make the most of the daily movements of the sun.
Another very valid example is the Intesa Sanpaolo office building which bears the signature of Renzo Piano. The building is powered by electricity produced from renewable sources and 1,600 m2 of photovoltaic panels and is the greenest skyscraper in Italy.

Photo: hansenn on Depositphotos.com

Photo: hansenn on Depositphotos.com
Other BIPV elements
In addition to photovoltaic facades, there are other elements that can make the building even more eco-sustainable.
Photovoltaic balcony parapets, photovoltaic roof tiles, photovoltaic canopies and photovoltaic balustrades are just some examples of architecturally integrated photovoltaics.
“The most important element of inspiration for architects today is the fragility of the earth. It is a sign of dynamism, a way of looking at tomorrow without being terrified by it. After all, the future is the only place where we can go.”
Renzo Piano