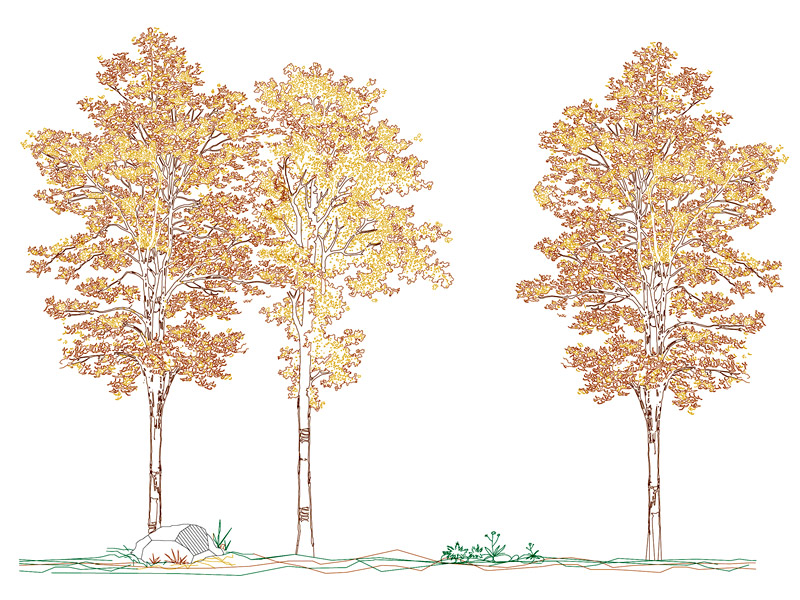
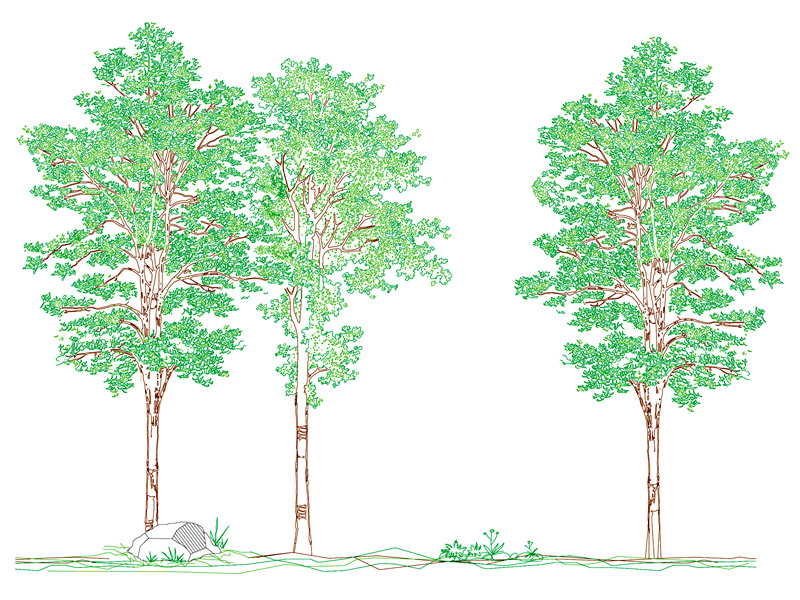
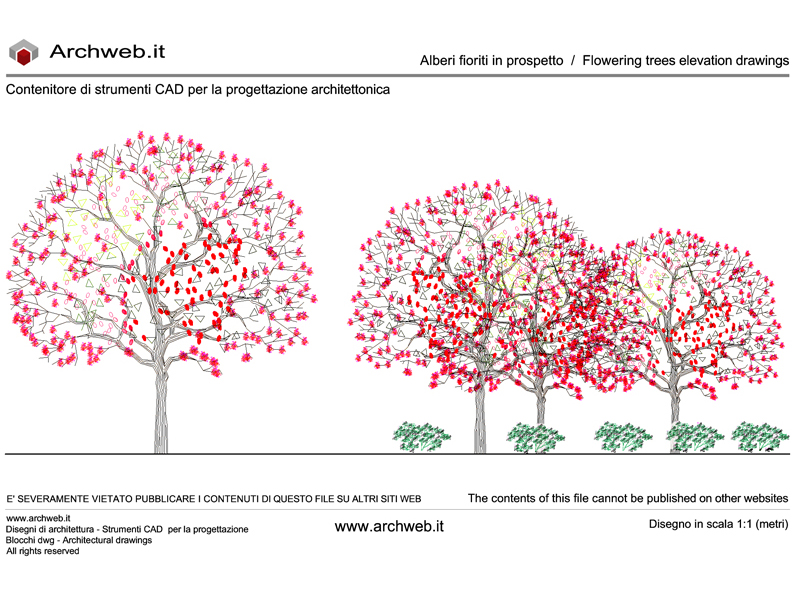
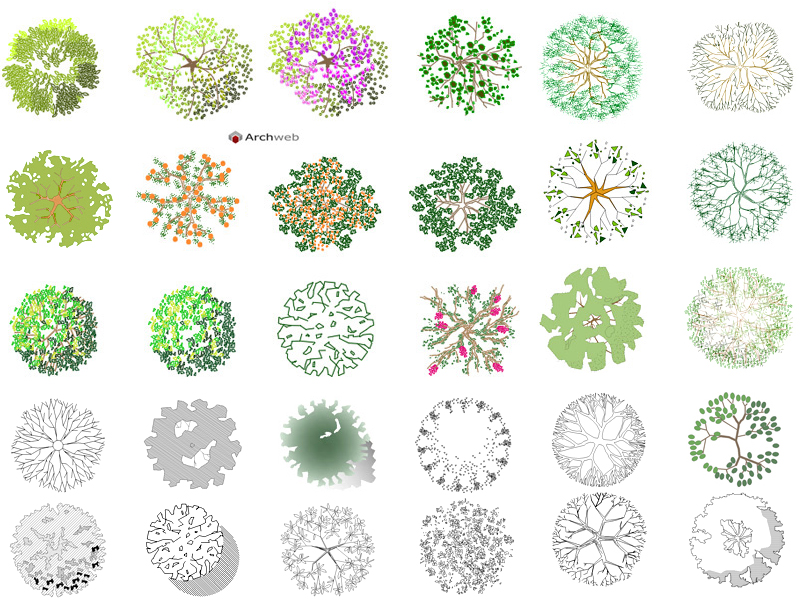
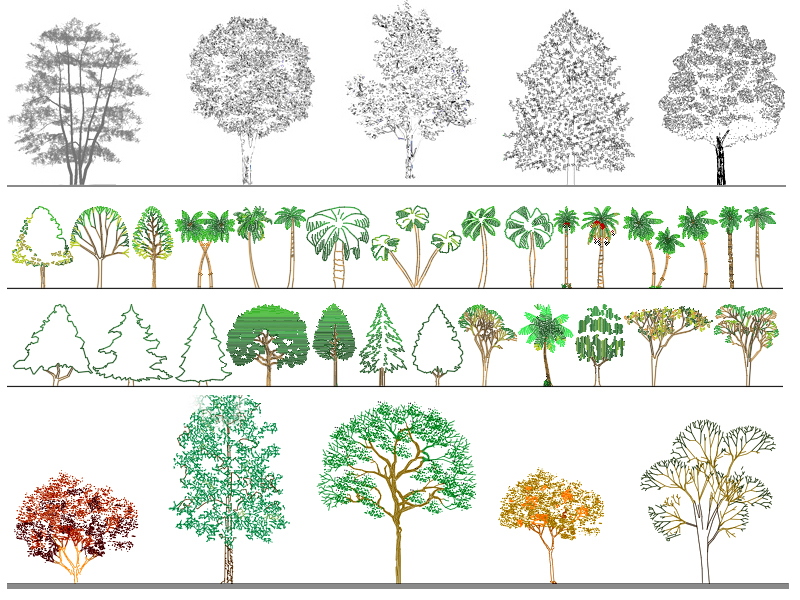
Road trees
The road trees recall nature within the cities
Road trees recall nature within cities and mitigate the impact of vehicular traffic in peripheral areas and in the countryside. In urban contexts they embellish busy areas, perform urban furnishing functions, but perform other very important functions.
They contain the risks of flooding, since among foliage, branches, trunks and roots, they are able to consistently absorb rainwater, especially when there are multiple rows.
The trees allow for the cooling of the air, both because the foliage intercepts solar radiation and offers shade, and because it produces steam that subtracts thermal energy from the surrounding environment.
Plants contain carbon dioxide and various gases as the leaf plate is able to absorb the particulate matter released by vehicles, performing an important filter function and helping to contain the ozone hole.
However, putting trees in the city cannot be considered a simplistic solution because the trees can contain the beneficial breezes and change the humidity of the area. The choice of trees should therefore be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, examining the characteristics and extent of the area in which to place them, choosing the aesthetic and formal characteristics of the plants, such as the appearance of the canopy, flowering, persistence of the foliage over the year and it is also very important, in the design phase, to take into account the maintenance, extension and characteristics of the root system in order to prefigure the evolutionary scenarios in the short, medium and long term. The extension of the canopy of the trees must guide the right distance between the plants, between the plants and buildings and other human activities. It is also necessary to keep in mind how much the inflorescences, the foliage or the fruit generated, can affect the normal paths.
In fact, each plant has its own potential for growth and therefore requires adequate space, both at the top and at the base. It is not uncommon for the roots to conflict with ducts and underground utilities, or the canopy to generate problems with overhead lines such as electricity, telephone and public lighting.
The plants with greater expansion, such as oaks, linden trees and ash trees, reach a crown of 15 meters, the alders, maples, hornbeams, can reach a crown of 10 meters, while less extension have plants of the rosaceae. There are plants whose crown extension reaches up to 6 meters but with a columnar pattern, such as cypresses.
Some plant parasites are present in urban environments because the relationship with nature that allows the containment of pathogens is lacking. To prevent particular environmental conditions, climate changes or diseases from causing plant problems, it is best to use varieties of native species and carefully evaluate the use of exotic plants and their ability to acclimatize.
Furthermore, it is not only useful to design a good irrigation system, choice and placement of plants, but also to foresee and plan the management of the arboreal heritage over time, because they are living organisms whose state of health must be monitored to prevent ruinous falls, avoiding , with sudden pruning and radical amputations, to worsen the living conditions of the plants.