The suspended ceiling
History - Use - Characteristics - Types and materials
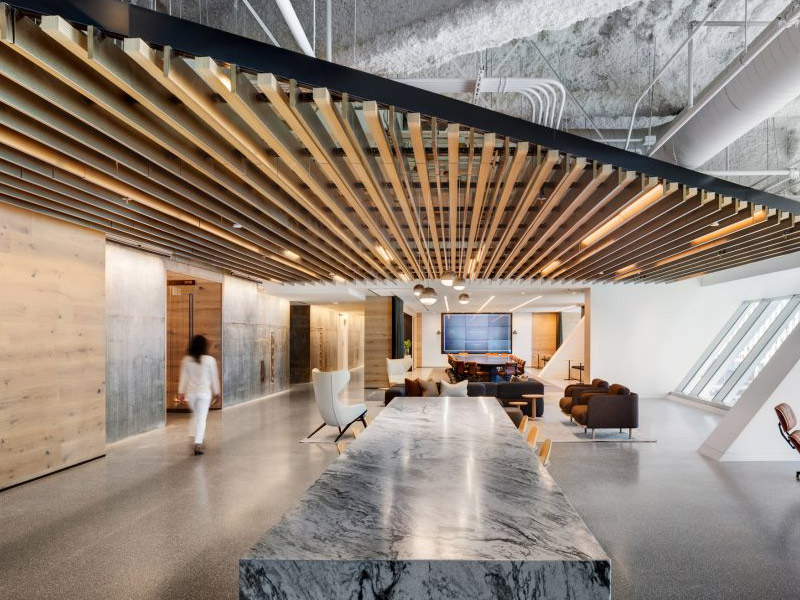

The suspended ceiling is a construction work consisting of a flat horizontal structure placed at a lower level than the attic or roof. This is a light accessory work through which we can modify and enrich the environments quickly and effectively.
Its use in recent times arises from the need to hide or cover architectural elements such as beams, electrical and plumbing systems, which cannot be housed or embedded inside the attics or roofs and which would therefore be visible. Furthermore, its use has notable insulating and hygienic characteristics.
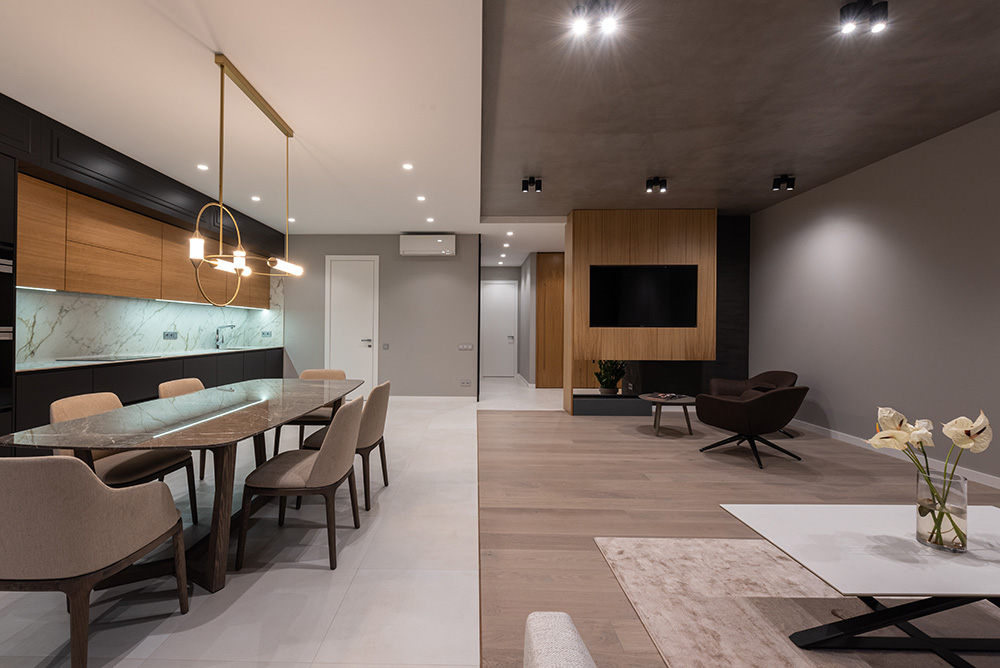

History
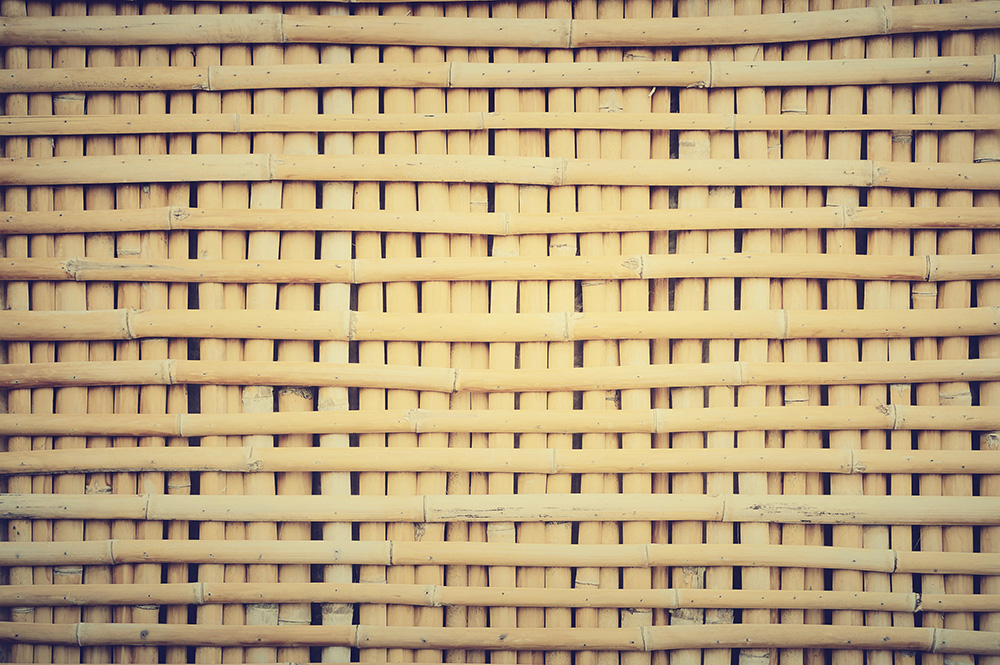
In less recent times, its use consisted in the creation of a light structure made up of wood and woven reeds, beneath which a layer of plaster was applied. The flexibility in the use of this material allowed the ceiling to be modeled by creating curved surfaces or more complex shapes, such as barrel vaults and sail vaults.

Function and use of false ceilings
In most cases, the false ceiling is made to house, within the space created between the light structure and the ceiling, one or more systems, such as the lighting, hydraulic and ventilation systems. also allowing the insertion of high-performance insulating panels, necessary to satisfy insulation and thermo-acoustic comfort needs.
The cladding of the structure is made with different types of heat-insulating and sound-absorbing materials, or with fire resistance characteristics, but as we have already mentioned, its functions can be of a purely aesthetic or technical nature, in fact inside it can be inserted the ventilation system for mechanical ventilation, in this case the false ceiling constitutes to all intents and purposes an equipped technical compartment in which pipes and ducts, electrical, hydraulic and telematic networks can be distributed, as well as machines such as the unit of mechanical ventilation. In this case it will be necessary for the false ceiling to be inspectable.
Like other construction works present in buildings, the false ceiling will have to respond to a series of parameters defined by legislation, it can prove to be an excellent solution for adapting existing structures to fire regulations, as specific products allow the creation of a fireproof false ceiling with adequate fire resistance. Furthermore, within this space, we can accommodate retractable ladders useful for making the attics accessible, or more simply it can be used to adjust the heights of the space. When calculating the useful height of a building, whether it is a new construction or an existing one, it will be necessary to take into consideration the minimum housing standards defined by the legislation, given that the introduction of a false ceiling will lead to a reduction in the useful height of the building local.
By useful height we mean the total useful height of a floor or room, represented by the net distance between the floor and the intrados of the ceiling or false ceiling. When calculating the net useful height of a room, the main beams, the thickness of the floors and/or structural elements that reduce the net useful distance of the floor must not be taken into consideration.
The minimum standard height established by law for homes is 2.70 m, while for corridors, hallways, bathrooms, toilets and closets, it can be reduced to 2.40 m.
Main characteristics of false ceilings:
- aesthetic rendering;
- adaptability of shape, materials, colors;
- ease of application;
- ease of maintenance;
- ease of use;
- variety in the choice of material;
- possibility of housing systems;
- possibility of housing insulating materials;
- flexibility in the insertion of lighting fixtures.
Furthermore, in relation to safety, CE legislation establishes that each individual element must comply with the following parameters:
- static and dimensional resistance;
- high flame retardant performance;
- high thermo-acoustic performances;
- high hygienic and sanitary performance.
Typology
The types of false ceilings can be divided into numerous categories and each of them can offer specific advantages and functionality. The main distinctions can be:
Based on their conformation, they are divided into:
- Continuous: made up of a single visual element, characterized by a hidden frame with gaps between the joints covered if it is plasterboard or glued together if it is other materials, this type of false ceiling cannot be inspected if made of plasterboard.
- Discontinuous: the individual elements can be dismantled for inspection and maintenance needs of the systems contained within.
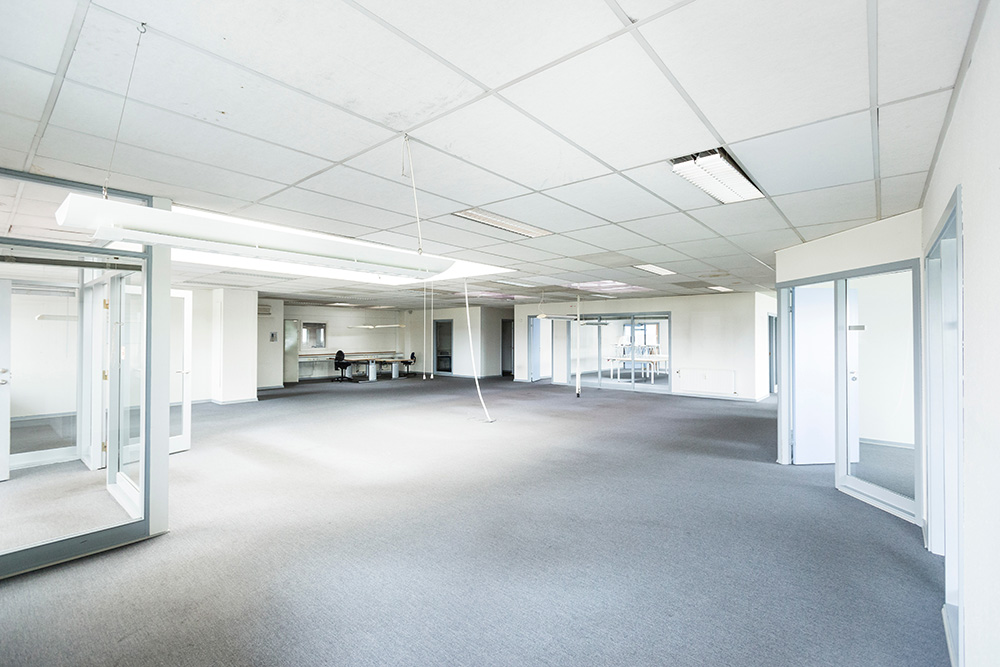

Based on technical performance, they are divided into:
- Heat insulating and sound absorbing
Present in public places such as theatres, concert halls, offices, lecture halls, etc. where it is necessary to satisfy a high degree of thermal or acoustic insulation or sometimes both. Examples of heat-insulating and sound-absorbing materials are rock wool and glass wool. - Fireproof: it is a material with high fire resistance characteristics. Used both in private homes and in public places.
It can be made of metal, wood, aluminum, fabric, plasterboard, PVC, etc.
Based on their aesthetic performance and functionality, they are divided into:
- Open: their function is mainly aesthetic, given that, as they do not form a closed compartment, it is not possible to insert any type of insulation.
- Inspectable: equipped with inspection hatches, they can be included in the category of removable false ceilings and are made up of elements that can be removed individually to access the interior in case of inspection.
- Not inspectable: they are made up of panels adhering to each other continuously.
- Coffered: usually introduced for acoustic insulation. They generally consist of large structures.
- Grids: the effect is that of a light but continuous false ceiling given that the panels, made in a modular manner, adhere to each other without the need to insert other materials in the joints.
- Paneled: they can be made of different materials such as aluminium, steel, wood, gypsum fibre, PVC
- Tesi: also made of PVC.
Most false ceilings allow us to insert modular lighting fixtures, air vents, smoke detectors, etc..
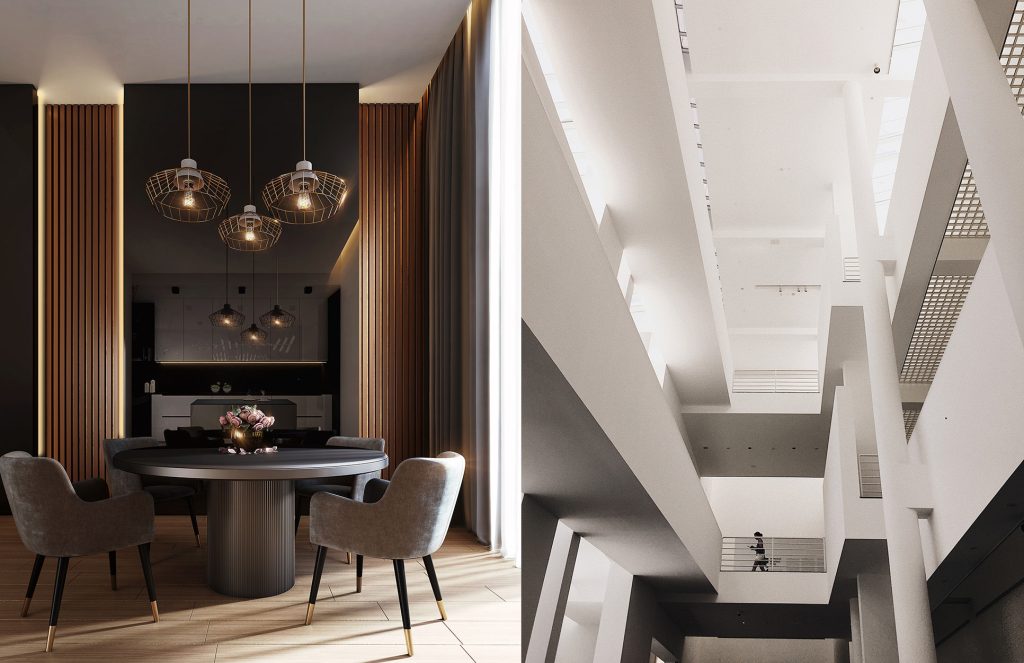

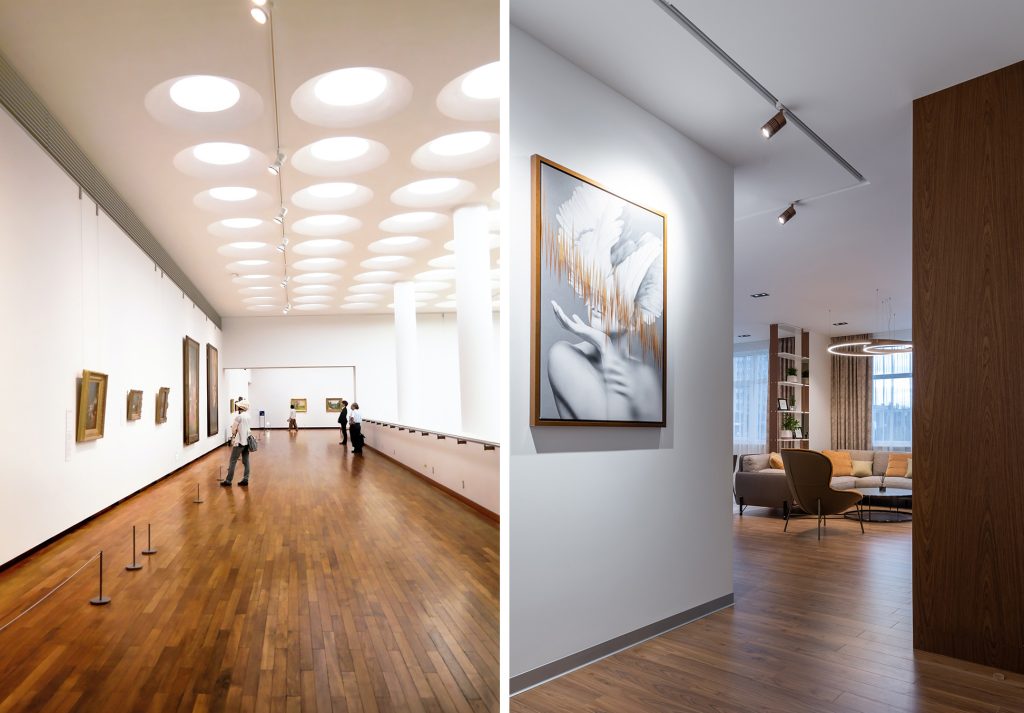
Right photo: example of inspectable grid false ceiling and continuous false ceiling – Source: Pexel
Warping or structure
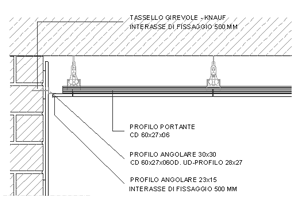
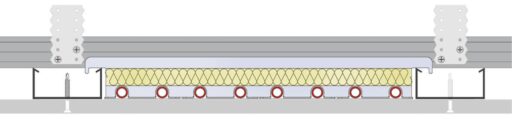
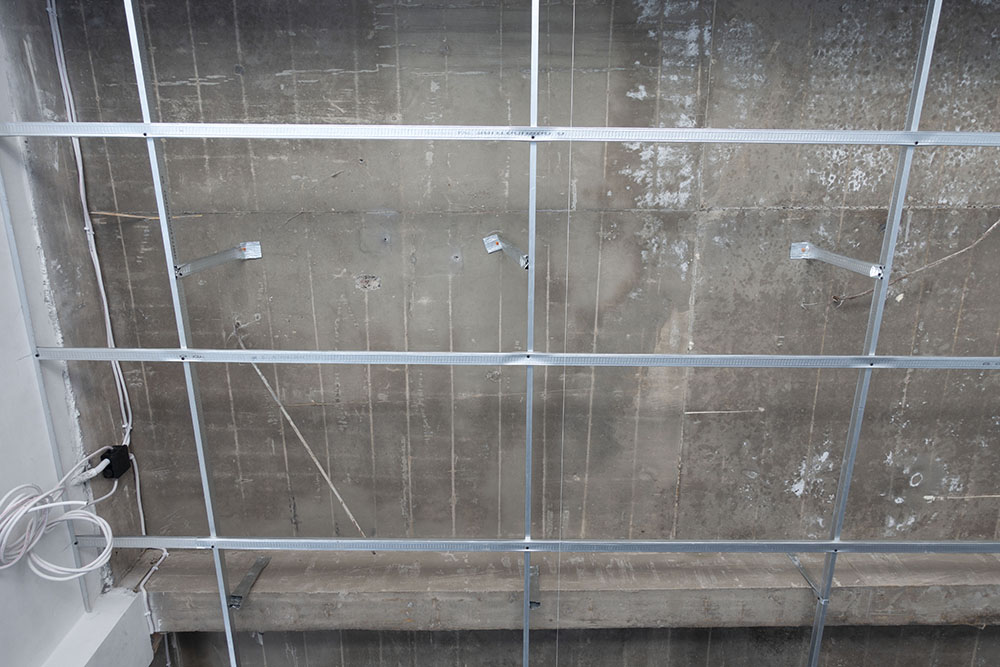
This is a suspended frame suitable for supporting the weight of the entire structure, which can be made either of wood or, more commonly, of metallic material.
The structure of the attic is made up of a set of framed support elements (bearing profiles in galvanized steel) and a closure or shielding depending on whether they are full or grid false ceilings, the frame is anchored below the intrados of an attic or a roof or along the perimeter walls.
Its anchoring occurs through the use of metal anchors and hooks to which the steel cables are fixed; the hangers and dowels have the task of supporting the entire structure.
The shielding is usually made with modular elements, which constitute a grid organized into square meshes with the exception of the curved areas where the covering material is most commonly modeled.
The suspended false ceiling must be created with a metal structure and adjustable hangers. In some cases, bracing may also be necessary, also made with metal elements (hangers), installed at 45°.
The false ceiling frame can be hidden, semi-hidden or visible:
- Hidden: its structure is located entirely above the last layer of covering material. The latter will indicate whether it is a closed or open false ceiling.
- Semi-hidden: its structure is only partially visible. The most common method is that achieved through the use of inverted T-shaped profiles on which modular panels are positioned that can be easily dismantled and inspected and which allow quick and easy dismantling in the case of ordinary or extraordinary maintenance of both the false ceiling and the elements housed inside it.
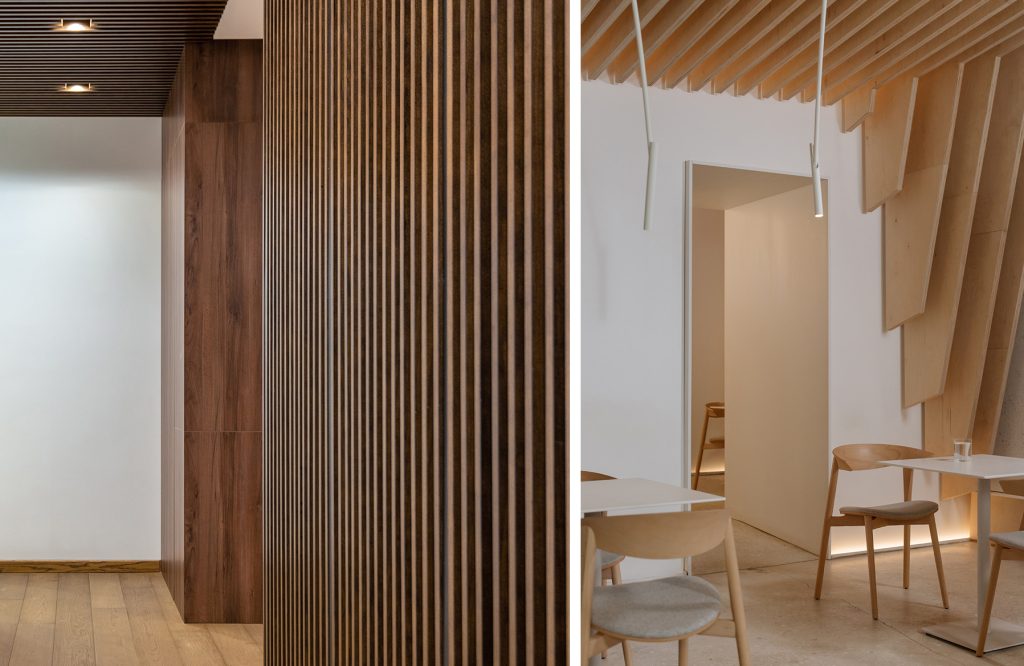
- At sight: Its structure is totally visible. Commonly used in offices and public places, although today it is often used inside homes when a high level of design is desired. The exposed structure consists of a wooden or steel structure beneath which different materials are positioned in the form of slats or other materials, arranged in a modular manner and maintaining a spaced pattern.
From this subdivision comes the definition of closed or open false ceiling.
You have a closed false ceiling when the structure is not visible, they generally consist of panels made of wood or plaster. While by open false ceiling we mean a false ceiling whose structure is visible and easily accessible.

Materials
Among the most widespread materials, the main one is certainly plasterboard which remains the most accessible in economic terms together with wood, which is decidedly more expensive, followed by polystyrene and mineral fibres. The false ceilings market offers solutions for any design and aesthetic need. But let’s now see what the main characteristics of false ceilings are based on the choice of material:
- Plasterboard false ceiling: suitable for any commercial or residential use; it is a very widespread building material in light construction and is made up of pressed plaster panels, enclosed within two sheets of cardboard, which in turn achieve certain performance characteristics depending on the solutions adopted. We can define it as a material with simple, linear and minimal characteristics, as well as particularly elastic, light and easy to use. The sheets always come in the form of thin panels of variable thickness depending on needs. Its diffusion in construction is due to the speed of execution that its use allows.The addition of additives can give the product a high degree of surface hardness, mechanical resistance and resistance in the presence of high levels of humidity; furthermore, the additives make it possible to give the panel high water-repellent and fire-resistance characteristics. The plaster that makes up the slabs is partially dehydrated into which glass fibers, perlite and vermiculite are inserted.
Thanks to the use of plasterboard sheets, it is also possible to easily model curvilinear shapes. - Mineral fiber false ceiling: this is a product containing rock wool or glass fibres, developed specifically for the acoustic correction of rooms.
- Wooden false ceilings: gives a warm tone to the environment in which it is used, very common for both homes and offices that require an extra touch of elegance.Wood is a naturally occurring material, easy to work with and apply. A wooden false ceiling can be created using exclusively wood both for the construction of the frame and for the infill or alternatively you can opt for a mixed false ceiling with wooden cladding and load-bearing frame of other material. Wood is also a highly insulating material and lends itself to a wide range of uses for both residential and civil buildings. The use of wood has ancient origins given the ease of finding the material.Natural wood alone can increase the thermo-acoustic insulation of the roof or attic and also reduces humidity problems. Wooden false ceilings can be slatted or coffered.
- Aluminum and steel false ceilings: suitable for offices and public buildings both for their versatility and for the vast choice of solutions available on the market. They can range from linear ones, to thin and wide ones or alternatively open cell ones. Curvilinear panels can also be found on the market.
- PVC false ceilings: PVC false ceilings have high performance with regards to humidity in the rooms and can come in the form of slats and squares, with different surface finishes such as mirrors, shiny, opaque, colored material, etc..
- Tensioned PVC: it is a decorative material that can be molded under the effect of heat. For this type of false ceiling, as for all the others, it will be necessary to design the entire structure ad hoc, making use of highly specialized suppliers and manpower.
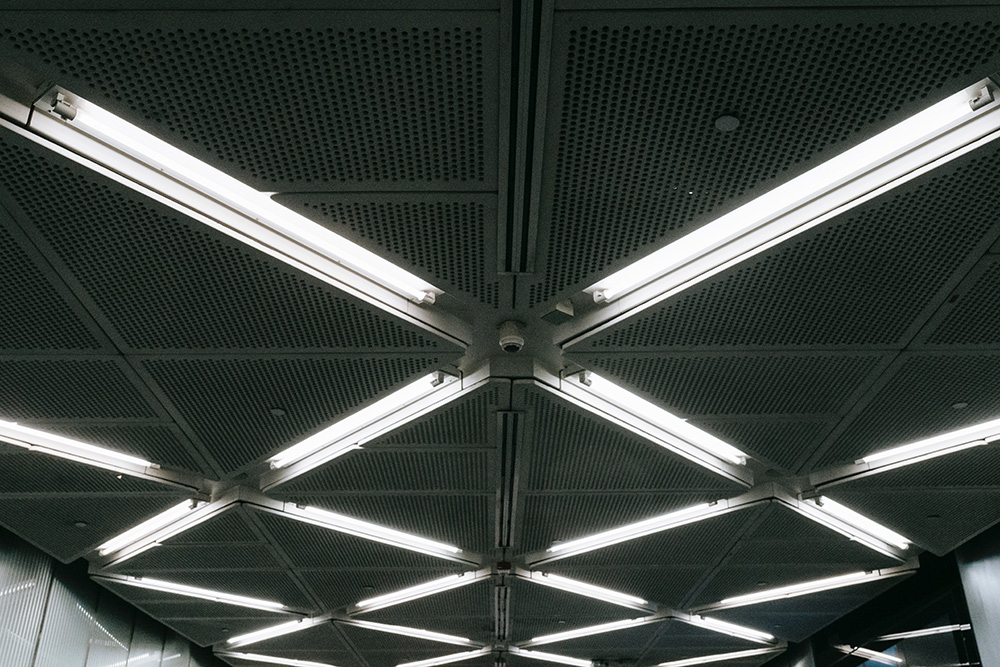


Maintenance and control of the false ceiling in public and private buildings
The control and maintenance of all building works is important for safeguarding the environment and people’s safety.
But what are the necessary checks that must be carried out during an inspection or verification of the health of a false ceiling? Let’s start by saying that the controls arise already in the design phase and during the execution of the work, in any case it will be essential to take the following checks into consideration:
- stability control of the slabs;
- control of the anchoring system of the structure, such as the number of hangers present;
- control of the center distances of the structure;
- verifies that during the installation phase, the installer has carried out the fastening of each component in a workmanlike manner according to the provisions of the technical data sheet provided by the manufacturer;
- presence of cracks, defects, detachments, deformations, breakages and/or failures of the structure or closing panels;
- presence of accidental weights placed above the slabs;
- correct execution of the positioning of the lighting fixtures.
The main causes of total or partial collapse of a false ceiling can be:
- presence of external factors that can compromise the performance guaranteed by both the manufacturer and the installer such as, for example, significant infiltrations from upper floors or roofs;
- unsuitable or poor maintenance;
- improper execution during the installation process;
- decay or aging of materials.

Seismic behavior of the false ceiling
Seismic risk is determined by the combination of 3 factors such as: hazard, vulnerability and exposure.
- Hazardousness = strength and frequency of an earthquake.
- Vulnerability = reaction capacity of the structure based on the damage it can suffer during a seismic event, given a certain density.
- Exhibition = nature of the exposed element (such as cultural, historical and artistic assets inside a museum) and of the people, due to the population density whether we are referring to a building for public use or to a building private.
During the design phase, the intended use of the building must be taken into consideration, whether it is a public or private place, in both cases it is within the designer’s discretion to create earthquake-resilient buildings, this resilience is achieved through a ‘adequate design as well as through the use of suitable materials, with high resistance to stress characteristics; characteristics necessary to make them operational both during and after the catastrophic event.
The anti-seismic legislation regulates the minimum requirements for checking the components of a building, including false ceilings.
All primary and secondary elements, structural or non-structural together with the systems, must be taken into consideration during the design phase.
These considerations also apply to false ceilings; in fact, when a building is subjected to an earthquake, whether it is inside an office, a hospital, a school or a home, the fall of material from the ceiling can jeopardize the safety and security of objects and objects. people, it is enough to know that the materials must also have a certain mechanical resistance.
What is mechanical strength or breakdown voltage? Mechanical resistance indicates the maximum stress that a given material is able to resist before its failure occurs.
False ceiling lighting
False ceiling lighting represents a fundamental aspect in the design of an environment. Depending on the type of lighting that will be integrated, countless lighting effects can be obtained. Lighting effects have always contributed to the transformation of a space, giving the environment a unique, original and welcoming appearance.
A first distinction regarding lighting must be made depending on whether it is natural or artificial light sources. In both cases, natural and artificial lights can be distinguished between direct and indirect lighting sources.
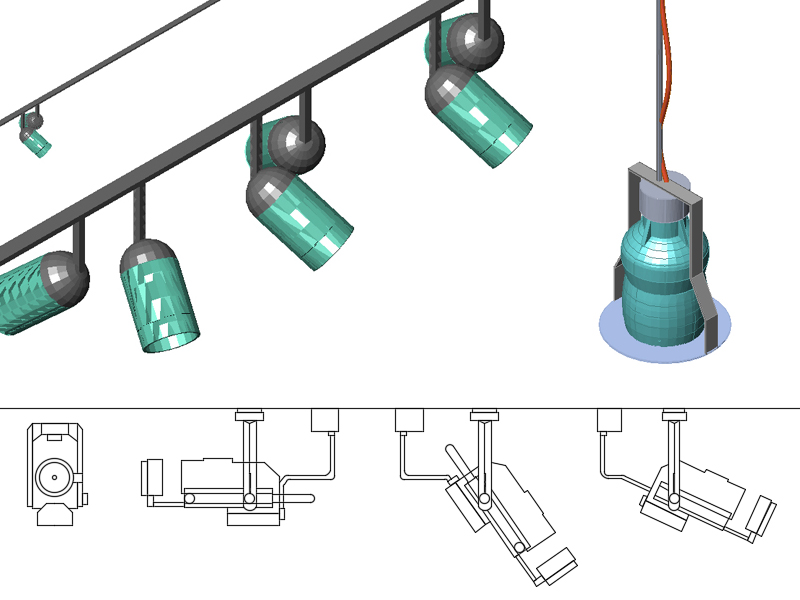
Direct lighting sources emit a more direct light flow towards an object or a specific limited area, but sometimes they can be very intense in some points and almost zero in others, thus generating a clear contrast between the illuminated and shadowed areas. An example of direct lighting sources are fixed spotlights or downlight luminaires. These are directional luminaires, as the beam of light emitted is directed downwards or towards a specific object, let’s try to think for example of a work of art inside a museum on which a lighting engineering study is carried out through which with adequate directional light sources, the work can be highlighted, also defining the perception that the human eye will have on it.
In work environments, direct lights are recommended when carrying out tasks that require particular attention, think of a laboratory where small components are made, on which it will be necessary to have a direct light source. In this case, in addition to the diffused lighting coming from the false ceiling, it will be necessary to integrate direct artificial light sources into the workstations.
An indirect light, on the other hand, will be more diffused, guaranteeing homogeneous lighting throughout the room. In fact, this type of lighting allows the light to be distributed uniformly throughout the entire room. To date, indirect light represents the best solution for offices, where a high level of concentration is required to guarantee the performance of tasks during working hours. Indirect lights are also widely used in warehouses or alternatively in hospitals, schools, etc. in short, in those places where you want to create a warm and welcoming environment.
A further distinction can be made depending on the tone of the colors emitted by the light, which can be divided into warm light, natural light and cold light. Light sources are perceived by the human eye through a light color temperature scale defined in degrees Kelvin (K). This gradation is represented by a color scale that goes from red/orange, through white to blue. The closer you are to red, the warmer the light is considered. However, if the shade is close to white, we can consider it neutral, while as we get closer to blue, the light is considered cold.

Types of lighting based on the position of the LED light
Light cuts: these are real cuts, in which, with the use of an aluminum profile, LED strips are inserted which run along the entire length of the cut.
Throat: the throat is created by a recess in the false ceiling in which a LED strip is positioned.
Floating false ceiling: this is a hanging false ceiling, the dimensions of which can be similar to those of the room or alternatively if it is a portion of the false ceiling, the space will be very close to the wall creating a small area in which to place the lighting body, the latter will project its light towards the wall, creating a light diffusion effect.
Plasterboard offers multiple solutions that can be adopted both according to the volumes that will be created and in terms of light level; its versatility allows you to more easily diversify the lighting effect you want to obtain, without however having to resort to the use of other lighting elements such as wall lamps, ceiling lights or suspended chandeliers, which in the absence of adequate lighting coming from the false ceiling, may be necessary to achieve the minimum comfort levels established by law. The plasterboard false ceiling can accommodate any type of lighting, from LED to point lights.
Types of luminous elements
Depending on needs, the false ceiling can be integrated with: fixed, adjustable, recessed, external spotlights, LED light, chandeliers, ceiling lights, etc. Whatever the solution, it is important to harmonize the elements with each other, creating a perfect combination of shapes, geometries, functionality, materials and lighting.

Integration of lighting in offices
In offices and any work environment, the legislation establishes that lighting must be sufficient and guarantee adequate contrast based on the tasks to be carried out.
The workstations must be correctly lit and directed towards both natural and artificial light sources. But unlike homes, offices require particular precautions, given that they should guarantee the high quality standards necessary for carrying out work in an optimal comfort situation, for example, try to think about the case in which the work is carried out using technological equipment /video terminals; in this case it will be necessary to guarantee a lighting level that avoids any eye strain or glare caused by the positioning and intensity of the light source. The light in the work environments must guarantee a homogeneous distribution of lighting, facilitating concentration and best facilitating productivity without causing disturbances to the worker.
The use of modular false ceilings is very common in offices and work environments; in most cases, the modules are arranged in an alternating linear manner and can be directly installed into the frame through different interlocking methods.

Whether it is plasterboard, wood, PVC, stretched PVC or other materials, the false ceiling is a versatile element with multiple performances and can also be defined based on the type of lighting that will be integrated into it. Its use provides numerous advantages and countless functional and aesthetic results can be achieved.