The vertical gardens
Classification, species, types of greenery, support structures
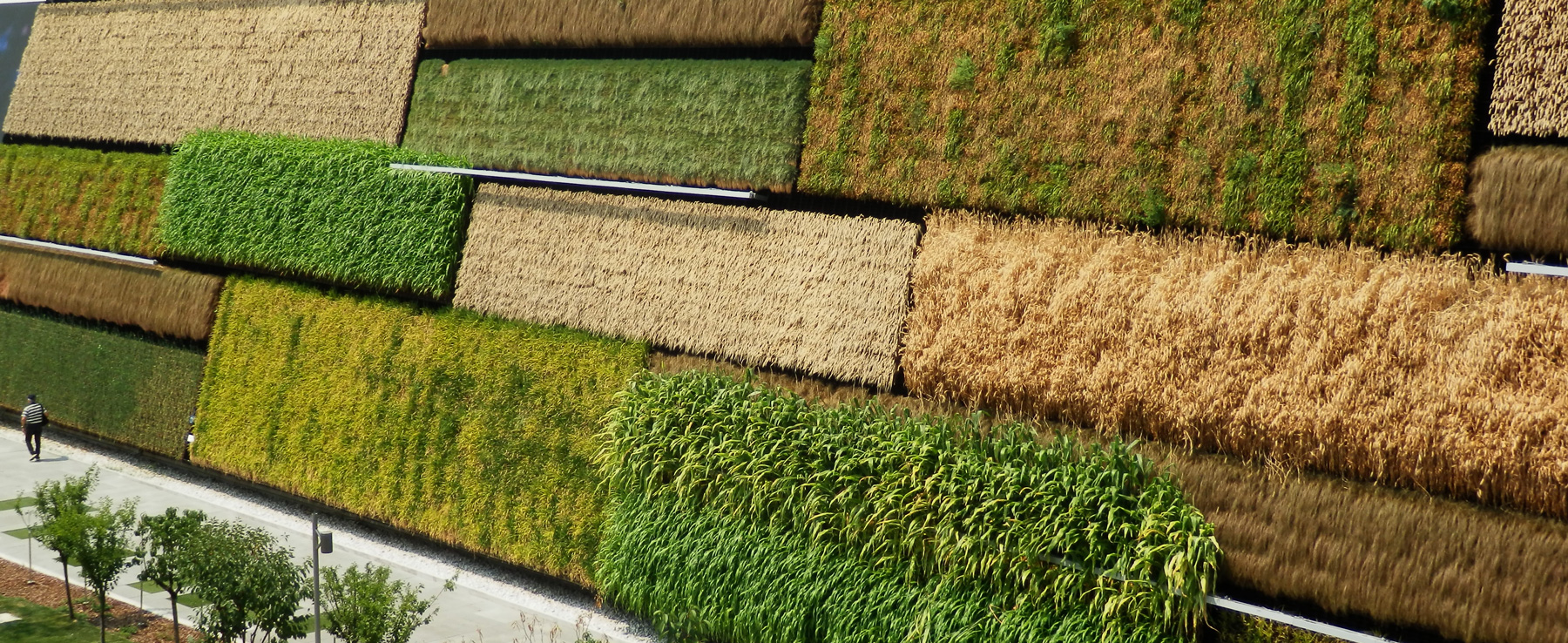

Classification, species, types of greenery, support structures and advantages
For “Vertical Garden” means a facade or a wall of a building covered with plant plants.
In this way the garden becomes an integrated component that can be installed anywhere: it is a structure especially suitable for homes in the city, where the limited space does not always allow the presence of a real environment dedicated to greenery.
The development of this type of structure is due in particular to the French botanist Patrik Blanc, and his studies concerning continuous rooting surface systems in hydroponics, the so-called Blanc system, characterized by a lower buffer capacity, a limited size and a system equipped with an air filter. Thanks to his very innovative experiments, Blanc was able to reproduce on the walls of numerous European buildings colorful and suggestive plant compositions typical of subtropical forests, revolutionizing the very idea of ”vertical garden”, which had existed until that moment.
One of the first reasons for the birth of the system is an aesthetic one, since a vegetal cladding certainly gives an added value to a building facade; there is also a reason linked to the increasingly frequent demand in recent years for technologies with low environmental impact.
The plants of the green walls usually have climbing characteristics and are clinging directly to the building structure through vertical supports belonging to the facade itself.
In this way the vertical garden constitutes a sort of “skin” of the building, since like the skin of man, it fulfills the task of protection and thermohygrometric regulation of the building itself.
Continue reading the full article
by Denise Barbaroux


VERTICAL GREEN
What is vertical green roof?
Vertical greenery has taken hold in recent years and is becoming a constant element in architectural projects, both in new buildings and in renovations.
The green wall, forming a kind of ‘second skin’ of the building, has some advantages:
- improved insulation as it prevents direct radiation of sunlight on the wall, which does not heat up and does not radiate heat inside;
- reduction of heat loss from buildings to the outside, thanks to the effect of thermal mass.
In addition, it contributes to the reduction of fine dust, which it manages to capture through the foliar apparatus, and finally has a significant aesthetic and ornamental impact.
How and where to make it?
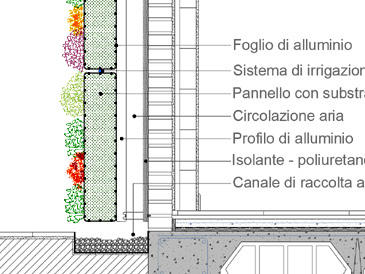
The creation of a green wall starts from the choice of the type of plant system and the support structure. We can essentially identify two types:
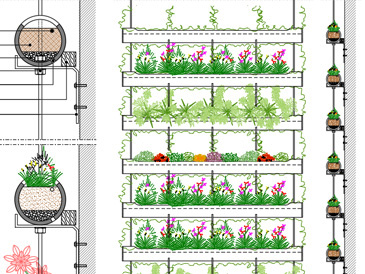
- vertical greenery achieved through climbing plants. It exploits the ability of plants to cling to adequate support structures to constitute what is in effect a green screen;
- vertical gardens, realized by inserting among the species not only climbing ones, but also plants and small shrubs.
For both categories, in principle, it is necessary:
- choose the most suitable species, also in consideration of the climate;
- provide a geotextile or a geocomposed non-woven fabric mat containing the cultivation substrate;
- create a supporting structure for the plants, usually in steel (light grating with uprights in the first case, bars fixed to the wall in the second, which incorporate mattress and geotextile);
- provide for an irrigation system.
Albedo: 0,2
Maintenance:
- periodic replacement of plants
- irrigation
Sources and useful links:
http://www.verticalgardenpatrickblanc.com
https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Giardino_verticale
Vertical greening systems for urban architecture (by Luca Siracusa) >
Regenerate the city with nature
Tools for the design of public spaces between mitigation and adaptation to climate change
Valentina Dessì, Elena Farnè, Luisa Ravanello, Maria Teresa Salomoni